Rationale and design of the Kanyini guidelines adherence with the polypill (Kanyini-GAP) study: a randomised controlled trial of a polypill-based strategy amongst indigenous and non indigenous people at high cardiovascular risk
- PMID: 20687931
- PMCID: PMC2923109
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2458-10-458
Rationale and design of the Kanyini guidelines adherence with the polypill (Kanyini-GAP) study: a randomised controlled trial of a polypill-based strategy amongst indigenous and non indigenous people at high cardiovascular risk
Abstract
Background: The Kanyini Guidelines Adherence with the Polypill (Kanyini-GAP) Study aims to examine whether a polypill-based strategy (using a single capsule containing aspirin, a statin and two blood pressure-lowering agents) amongst Indigenous and non-Indigenous people at high risk of experiencing a cardiovascular event will improve adherence to guideline-indicated therapies, and lower blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
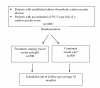
Methods/design: The study is an open, randomised, controlled, multi-centre trial involving 1000 participants at high risk of cardiovascular events recruited from mainstream general practices and Aboriginal Medical Services, followed for an average of 18 months. The participants will be randomised to one of two versions of the polypill, the version chosen by the treating health professional according to clinical features of the patient, or to usual care. The primary study outcomes will be changes, from baseline measures, in serum cholesterol and systolic blood pressure and self-reported current use of aspirin, a statin and at least two blood pressure lowering agents. Secondary study outcomes include cardiovascular events, renal outcomes, self-reported barriers to indicated therapy, prescription of indicated therapy, occurrence of serious adverse events and changes in quality-of-life. The trial will be supplemented by formal economic and process evaluations.
Discussion: The Kanyini-GAP trial will provide new evidence as to whether or not a polypill-based strategy improves adherence to effective cardiovascular medications amongst individuals in whom these treatments are indicated.
Trial registration: This trial is registered with the Australian New Zealand Clinical Trial Registry ACTRN126080005833347.
References
-
- Vos T, Barker B, Stanley L, Lopez A. The burden of disease and injury in Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples 2003. Brisbane: The University of Queensland; 2007. - PubMed
-
- National Heart Foundation of Australia, Cardiac Society of Australia and New Zealand. Reducing risk in heart disease 2004. National Heart Foundation of Australia; 2005.
-
- National Heart Foundation of Australia. Hypertension management guide for doctors. National Heart Foundation; 2004.
-
- National Stroke Foundation. Clinical guidelines for the management of acute stroke. National Stroke Foundation; 2002.
-
- New Zealand Guidelines Group. New Zealand Cardiovascular Guidelines Handbook: A summary resource for primary care practitioners. 2. Wellington: New Zealand Guidelines Group; 2009.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous