Suppression of colitis-driven colon cancer in mice by a novel small molecule inhibitor of sphingosine kinase
- PMID: 20688834
- PMCID: PMC2981458
- DOI: 10.1093/carcin/bgq158
Suppression of colitis-driven colon cancer in mice by a novel small molecule inhibitor of sphingosine kinase
Abstract
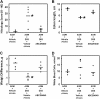
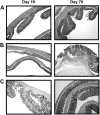
Sphingolipid metabolism is driven by inflammatory cytokines. These cascade of events include the activation of sphingosine kinase (SK), and subsequent production of the mitogenic and proinflammatory lipid sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P). Overall, S1P is one of the crucial components in inflammation, making SK an excellent target for the development of new anti-inflammatory drugs. We have recently shown that SK inhibitors suppress colitis and hypothesize here that the novel SK inhibitor, ABC294640, prevents the development of colon cancer. In an azoxymethane (AOM)/dextran sulfate sodium (DSS) mouse model, there was a dose-dependent decrease in tumor incidence with SK inhibitor treatment. The tumor incidence (number of animals with tumors per group) in the vehicle, ABC294640 (20 mg/kg) and ABC294640 (50 mg/kg) groups were 80, 40 and 30%, respectively. Tumor multiplicity (number of tumors per animal) also decreased from 2.1 ± 0.23 tumors per animal in the AOM + DSS + vehicle group to 1.2 ± 0 tumors per animal in the AOM + DSS + ABC294640 (20 mg/kg) and to 0.8 ± 0.4 tumors per animal in the AOM + DSS + ABC294640 (50 mg/kg) group. Importantly, with ABC294640, there were no observed toxic side effects. To explore mechanisms, we isolated cells from the colon (CD45-, representing primarily colon epithelial cells) and (CD45+, representing primarily colon inflammatory cells) then measured known targets of SK that control cell survival. Results are consistent with the hypothesis that the inhibition of SK activity by our novel SK inhibitor modulates key pathways involved in cell survival and may be a viable treatment strategy for the chemoprevention colitis-driven colon cancer.
Figures
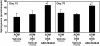

Similar articles
-
Effects of triptolide on the sphingosine kinase - Sphingosine-1-phosphate signaling pathway in colitis-associated colon cancer.Int Immunopharmacol. 2020 Nov;88:106892. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106892. Epub 2020 Aug 15. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32810834
-
Antitumor activity of sphingosine kinase 2 inhibitor ABC294640 and sorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma xenografts.Cancer Biol Ther. 2011 Mar 1;11(5):524-34. doi: 10.4161/cbt.11.5.14677. Epub 2011 Mar 1. Cancer Biol Ther. 2011. PMID: 21258214 Free PMC article.
-
The Sphingosine Kinase 2 Inhibitor ABC294640 Restores the Sensitivity of BRAFV600E Mutant Colon Cancer Cells to Vemurafenib by Reducing AKT-Mediated Expression of Nucleophosmin and Translationally-Controlled Tumour Protein.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 5;22(19):10767. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910767. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34639107 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of ulcerative colitis in mice by orally available inhibitors of sphingosine kinase.Dig Dis Sci. 2008 Apr;53(4):997-1012. doi: 10.1007/s10620-007-0133-6. Epub 2007 Dec 4. Dig Dis Sci. 2008. PMID: 18058233 Free PMC article.
-
Murine Model for Colitis-Associated Cancer of the Colon.Methods Mol Biol. 2016;1438:245-54. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-3661-8_14. Methods Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 27150094 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The induction of microRNA-16 in colon cancer cells by protein arginine deiminase inhibition causes a p53-dependent cell cycle arrest.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e53791. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053791. Epub 2013 Jan 7. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23308284 Free PMC article.
-
Chemopreventive Effects of Polysaccharides and Flavonoids from Okra Flowers in Azomethane/Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Murine Colitis-Associated Cancer.Nutrients. 2023 Nov 17;15(22):4820. doi: 10.3390/nu15224820. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 38004214 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of sphingosine kinase 2 deficiency on the development of TNF-alpha-induced inflammatory arthritis.Rheumatol Int. 2013 Oct;33(10):2677-81. doi: 10.1007/s00296-012-2493-2. Epub 2012 Aug 3. Rheumatol Int. 2013. PMID: 23011090 Free PMC article.
-
Novel chemotherapeutic drugs in sphingolipid cancer research.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2013;(215):211-38. doi: 10.1007/978-3-7091-1368-4_12. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23579458 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel role of sphingosine kinase-1 in the invasion and angiogenesis of VHL mutant clear cell renal cell carcinoma.FASEB J. 2015 Jul;29(7):2803-13. doi: 10.1096/fj.15-270413. Epub 2015 Mar 24. FASEB J. 2015. PMID: 25805832 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

