Identification of microRNAs during rat liver regeneration after partial hepatectomy and modulation by ursodeoxycholic acid
- PMID: 20689055
- PMCID: PMC2957332
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00216.2010
Identification of microRNAs during rat liver regeneration after partial hepatectomy and modulation by ursodeoxycholic acid
Abstract
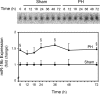
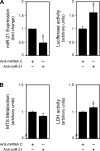
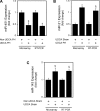
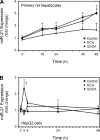
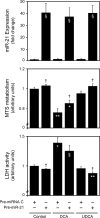
New gene regulation study tools such as microRNA (miRNA or miR) analysis may provide unique insights into the remarkable ability of the liver to regenerate. In addition, we have previously shown that ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) modulates mRNA levels during liver regeneration. Bile acids are also homeotrophic sensors of functional hepatic capacity. The present study was designed to determine whether miRNAs are modulated in rats following 70% partial hepatectomy (PH) and elucidate the role of UDCA in regulating miRNA expression during liver regeneration (LR). Total RNA was isolated from livers harvested at 3-72 h following 70% PH or sham operations, from both 0.4% (wt/wt) UDCA and control diet-fed animals. By using a custom microarray platform we found that several miRNAs are significantly altered after PH by >1.5-fold, including some previously described as modulators of cell proliferation, differentiation, and death. In particular, expression of miR-21 was increased after PH. Functional modulation of miR-21 in primary rat hepatocytes increased cell proliferation and viability. Importantly, UDCA was a strong inducer of miR-21 both during LR and in cultured HepG2 cells. In fact, UDCA feeding appeared to induce a sustained increase of proliferative miRNAs observed at early time points after PH. In conclusion, miRNAs, in particular miR-21, may play a significant role in modulating proliferation and cell cycle progression genes after PH. miR-21 is additionally induced by UDCA in both regenerating rat liver and in vitro, which may represent a new mechanism behind UDCA biological functions.
Figures


References
-
- Amaral JD, Castro RE, Solá S, Steer CJ, Rodrigues CM. p53 is a key molecular target of ursodeoxycholic acid in regulating apoptosis. J Biol Chem 282: 34250–34259, 2007. - PubMed
-
- Bandres E, Bitarte N, Arias F, Agorreta J, Fortes P, Agirre X, Zarate R, Diaz-Gonzalez JA, Ramirez N, Sola JJ, Jimenez P, Rodriguez J, Garcia-Foncillas J. microRNA-451 regulates macrophage migration inhibitory factor production and proliferation of gastrointestinal cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res 15: 2281–2290, 2009. - PubMed
-
- Barone M, Francavilla A, Polimeno L, Ierardi E, Romanelli D, Berloco P, Di Leo A, Panella C. Modulation of rat hepatocyte proliferation by bile salts: in vitro and in vivo studies. Hepatology 23: 1159–1166, 1996. - PubMed
-
- Bockhorn M, Goralski M, Prokofiev D, Dammann P, Grunewald P, Trippler M, Biglarnia A, Kamler M, Niehues EM, Frilling A, Broelsch CE, Schlaak JF. VEGF is important for early liver regeneration after partial hepatectomy. J Surg Res 138: 291–299, 2007. - PubMed
-
- Bostjancic E, Glavac D. Importance of microRNAs in skin morphogenesis and diseases. Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Panonica Adriat 17: 95–102, 2008. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

