Hypothalamic oxytocin mediates adaptation mechanism against chronic stress in rats
- PMID: 20689056
- PMCID: PMC2957337
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00483.2009
Hypothalamic oxytocin mediates adaptation mechanism against chronic stress in rats
Abstract
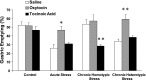
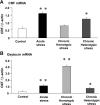
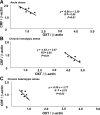
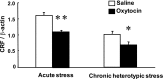
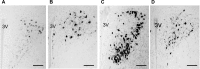
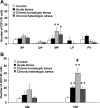
Accumulation of continuous life stress (chronic stress) often causes gastric symptoms. Although central oxytocin has antistress effects, the role of central oxytocin in stress-induced gastric dysmotility remains unknown. Solid gastric emptying was measured in rats receiving acute restraint stress, 5 consecutive days of repeated restraint stress (chronic homotypic stress), and 7 consecutive days of varying types of stress (chronic heterotypic stress). Oxytocin and oxytocin receptor antagonist were administered intracerebroventricularly (icv). Expression of corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) mRNA and oxytocin mRNA in the paraventricular nucleus (PVN) of the hypothalamus was evaluated by real-time RT-PCR. The changes of oxytocinergic neurons in the PVN were evaluated by immunohistochemistry. Acute stress delayed gastric emptying, and the delayed gastric emptying was completely restored after 5 consecutive days of chronic homotypic stress. In contrast, delayed gastric emptying persisted following chronic heterotypic stress. The restored gastric emptying following chronic homotypic stress was antagonized by icv injection of an oxytocin antagonist. Icv injection of oxytocin restored delayed gastric emptying induced by chronic heterotypic stress. CRF mRNA expression, which was significantly increased in response to acute stress and chronic heterotypic stress, returned to the basal levels following chronic homotypic stress. In contrast, oxytocin mRNA expression was significantly increased following chronic homotypic stress. The number of oxytocin-immunoreactive cells was increased following chronic homotypic stress at the magnocellular part of the PVN. Icv injection of oxytocin reduced CRF mRNA expression induced by acute stress and chronic heterotypic stress. It is suggested that the adaptation mechanism to chronic stress may involve the upregulation of oxytocin expression in the hypothalamus, which in turn attenuates CRF expression.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hypothalamic oxytocin attenuates CRF expression via GABA(A) receptors in rats.Brain Res. 2011 Apr 28;1387:39-45. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2011.02.091. Epub 2011 Mar 5. Brain Res. 2011. PMID: 21382355
-
Hypothalamic circuit regulating colonic transit following chronic stress in rats.Stress. 2012 Mar;15(2):227-36. doi: 10.3109/10253890.2011.614297. Epub 2011 Sep 21. Stress. 2012. PMID: 21936687
-
Beneficial effects of social attachment to overcome daily stress.Brain Res. 2010 Sep 17;1352:43-9. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2010.07.028. Epub 2010 Jul 17. Brain Res. 2010. PMID: 20643112
-
Central oxytocin is involved in restoring impaired gastric motility following chronic repeated stress in mice.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2010 Jan;298(1):R157-65. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00328.2009. Epub 2009 Nov 4. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2010. PMID: 19889866 Free PMC article.
-
Bridging the gap between GPCR activation and behaviour: oxytocin and prolactin signalling in the hypothalamus.J Mol Neurosci. 2011 Feb;43(2):200-8. doi: 10.1007/s12031-010-9452-8. Epub 2010 Sep 24. J Mol Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 20865346 Review.
Cited by
-
Paraventricular oxytocin neurons impact energy intake and expenditure: projections to the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis reduce sucrose consumption.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Sep 2;15:1449326. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1449326. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39286269 Free PMC article.
-
Stress Adaptation Upregulates Oxytocin within Hypothalamo-Vagal Neurocircuits.Neuroscience. 2018 Oct 15;390:198-205. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2018.08.021. Epub 2018 Aug 31. Neuroscience. 2018. PMID: 30176320 Free PMC article.
-
Environment and Behavior: Neurochemical Effects of Different Diets in the Calf Brain.Animals (Basel). 2019 Jun 14;9(6):358. doi: 10.3390/ani9060358. Animals (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31207977 Free PMC article.
-
Oxytocin Signaling Acts as a Marker for Environmental Stressors in Zebrafish.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 12;22(14):7459. doi: 10.3390/ijms22147459. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34299078 Free PMC article.
-
[Oxytocin and the mechanisms of alcohol dependence].Neuropsychiatr. 2018 Mar;32(1):1-8. doi: 10.1007/s40211-017-0229-y. Epub 2017 Jun 21. Neuropsychiatr. 2018. PMID: 28639210 Review. German.
References
-
- Abizaid A, Liu ZW, Andrews ZB, Shanabrough M, Borok E, Elsworth JD, Roth RH, Sleeman MW, Picciotto MR, Tschop MH, Gao XB, Horvath TL. Ghrelin modulates the activity and synaptic input organization of midbrain dopamine neurons while promoting appetite. J Clin Invest 116: 3229–3239, 2006. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ariga H, Nakade Y, Tsukamoto K, Imai K, Chen C, Mantyh C, Pappas TN, Takahashi T. Ghrelin accelerates gastric emptying via early manifestation of antro-pyloric coordination in conscious rats. Regul Pept 146: 112–116, 2008. - PubMed
-
- Ariga H, Tsukamoto K, Chen C, Mantyh C, Pappas TN, Takahashi T. Endogenous acyl ghrelin is involved in mediating spontaneous phase III-like contractions of the rat stomach. Neurogastroenterol Motil 19: 675–680, 2007. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

