HIF-1 mediates pathogenic inflammatory responses to intestinal ischemia-reperfusion injury
- PMID: 20689059
- PMCID: PMC2957330
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00065.2010
HIF-1 mediates pathogenic inflammatory responses to intestinal ischemia-reperfusion injury
Abstract
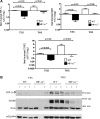
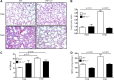
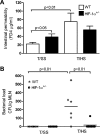
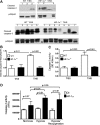
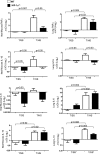
Acute lung injury (ALI) and the development of the multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS) are major causes of death in trauma patients. Gut inflammation and loss of gut barrier function as a consequence of splanchnic ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) have been implicated as the initial triggering events that contribute to the development of the systemic inflammatory response, ALI, and MODS. Since hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF-1) is a key regulator of the physiological and pathophysiological response to hypoxia, we asked whether HIF-1 plays a proximal role in the induction of gut injury and subsequent lung injury. Utilizing partially HIF-1α-deficient mice in a global trauma hemorrhagic shock (T/HS) model, we found that HIF-1 activation was necessary for the development of gut injury and that the prevention of gut injury was associated with an abrogation of lung injury. Specifically, in vivo studies demonstrated that partial HIF-1α deficiency ameliorated T/HS-induced increases in intestinal permeability, bacterial translocation, and caspase-3 activation. Lastly, partial HIF-1α deficiency reduced TNF-α, IL-1β, cyclooxygenase-2, and inducible nitric oxide synthase levels in the ileal mucosa after T/HS whereas IL-1β mRNA levels were reduced in the lung after T/HS. This study indicates that prolonged intestinal HIF-1 activation is a proximal regulator of I/R-induced gut mucosal injury and gut-induced lung injury. Consequently, these results provide unique information on the initiating events in trauma-hemorrhagic shock-induced ALI and MODS as well as potential therapeutic insights.
Figures


References
-
- Bakker WJ, Harris IS, Mak TW. FOXO3a is activated in response to hypoxic stress and inhibits HIF1-induced apoptosis via regulation of CITED2. Mol Cell 28: 941–953, 2007. - PubMed
-
- Bergeron M, Gidday JM, Yu AY, Semenza GL, Ferriero DM, Sharp FR. Role of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 in hypoxia-induced ischemic tolerance in neonatal rat brain. Ann Neurol 48: 285–296, 2000. - PubMed
-
- Bernaudin M, Nedelec A, Divoux D, MacKenzie E, Petit E, Schumann-Bard P. Normobaric hypoxia induces tolerance to focal permanent cerebral ischemia in association with an increased expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 and its target genes, erythropoietin and VEGF, in the adult mouse brain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 22: 393–403, 2002. - PubMed
-
- Bosch-Marce M, Okuyama H, Wesley J, Sarkar K, Kimura H, Liu Y, Zhang H, Strazza M, Rey S, Savino L, Zhou Y, McDonald K, Na Y, Vandiver S, Rabi A, Shaked Y, Kerbel R, LaVallee T, Semenza G. Effects of aging and hypoxia-inducible factor-1 activity on angiogenic cell mobilization and recovery of perfusion after limb ischemia. Circ Res 101: 1310–1318, 2007. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

