Transthyretin-related familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy-Progress in Kumamoto, Japan (1967-2010)-
- PMID: 20689228
- PMCID: PMC3066541
- DOI: 10.2183/pjab.86.694
Transthyretin-related familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy-Progress in Kumamoto, Japan (1967-2010)-
Abstract
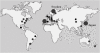
The authors reviewed contribution of Kumamoto University group to the progress of the studies on transthyretin (TTR)-related familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy (TTR-related FAP) for 42 years (from 1967 to 2009). Andrade (1952) first described a large group of patients with FAP in Portugal and Araki et al. (1967) in second discovered similar FAP patients in Arao, Kumamoto, Japan. Owing to progress in biochemical and molecular genetic analyses, FAP is now believed to occur worldwide. As of today, reports of about 100 different points of single or two mutations, or a deletion in the transthyretin (TTR) gene, have been published. The authors' group has made pioneer works for study of FAP in the world. The focus on therapy in amylodosis will increase sharply as an impetus in near future, and successful treatments are expected.
Figures



References
-
- Araki S. (1984) Type I familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy (Japanese type). Brain Dev. 6, 128–133 - PubMed
-
- Benson M.D. (1989) Familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy. Trends Neurosci. 12, 88–92 - PubMed
-
- Benson M.D., Uemichi T. (1996) Transthyretin amyloidosis. Amyloid 3, 44–56
-
- Ando Y., Araki S., Ando M. (1993) Transthyretin related amyloidosis. Intern. Med. 32, 920–922 - PubMed
-
- Andrade C. (1952) A peculiar form of peripheral neuropathy: Familial generalized amyloidosis with special involvement of the peripheral nerves. Brain 75, 408–427 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

