Interleukin 6 in autoimmune and inflammatory diseases: a personal memoir
- PMID: 20689230
- PMCID: PMC3066534
- DOI: 10.2183/pjab.86.717
Interleukin 6 in autoimmune and inflammatory diseases: a personal memoir
Abstract
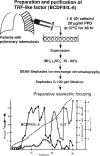
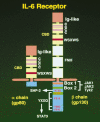
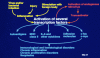
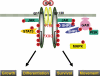
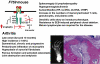
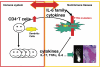
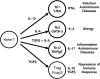
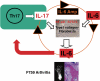
In this review, the author discusses the research that led to the identification and characterization of interleukin 6 (IL-6), including his own experience isolating IL-6, and the roles this cytokine has on autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. The cDNAs encoding B-cell stimulatory factor 2 (BSF-2), interferon (IFN)-beta2 and a 26-kDa protein were independently cloned in 1986, which in turn led to the identification of each. To resolve the confusing nomenclature, these identical molecules were named IL-6. Characterization of IL-6 revealed a multifunctional cytokine that is involved in not only immune responses but also hematopoiesis, inflammation, and bone metabolism. Moreover, IL-6 makes significant contributions to such autoimmune and inflammatory diseases as rheumatoid arthritis (RA).IL-6 activates both the STAT3 and SHP2/Gab/MAPK signaling pathways via the gp130 signal transducer. F759 mice, which contain a single amino-acid substitution in gp130 (Y759F) and show enhanced STAT3 activation, spontaneously develop a RA-like arthritis as they age. F759 arthritis is dependent on CD4(+) T cells, IL-6, and IL-17A, and is enhanced by the pX gene product from human T cell leukemia virus 1 (HTLV-1). Arthritis development in these mice requires that the F759 mutation is present in nonhematopoietic cells, but not in immune cells, highlighting the important role of the interaction between nonimmune tissues and the immune system in this disease. Furthermore, this interaction is mediated by the IL-6 amplifier through STAT3 and NF-kappaB. Ultimately, this model may represent a general etiologic process underlying other autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. More importantly, the understanding of IL-6 has paved the way for new therapeutic approaches for RA and other autoimmune and inflammatory diseases.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The point mutation of tyrosine 759 of the IL-6 family cytokine receptor gp130 synergizes with HTLV-1 pX in promoting rheumatoid arthritis-like arthritis.Int Immunol. 2004 Mar;16(3):455-65. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxh045. Int Immunol. 2004. PMID: 14978019
-
Autoimmune arthritis associated with mutated interleukin (IL)-6 receptor gp130 is driven by STAT3/IL-7-dependent homeostatic proliferation of CD4+ T cells.J Exp Med. 2006 Jun 12;203(6):1459-70. doi: 10.1084/jem.20052187. Epub 2006 May 22. J Exp Med. 2006. PMID: 16717113 Free PMC article.
-
A four-step model for the IL-6 amplifier, a regulator of chronic inflammations in tissue-specific MHC class II-associated autoimmune diseases.Front Immunol. 2011 Jun 16;2:22. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2011.00022. eCollection 2011. Front Immunol. 2011. PMID: 22566812 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting interleukin-6 in inflammatory autoimmune diseases and cancers.Pharmacol Ther. 2014 Feb;141(2):125-39. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2013.09.004. Epub 2013 Sep 27. Pharmacol Ther. 2014. PMID: 24076269 Review.
-
Pathophysiological roles for IL-18 in inflammatory arthritis.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2003 Dec;7(6):701-24. doi: 10.1517/14728222.7.6.701. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2003. PMID: 14640907 Review.
Cited by
-
NSAIDs/nitazoxanide/azithromycin repurposed for COVID-19: potential mitigation of the cytokine storm interleukin-6 amplifier via immunomodulatory effects.Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2022 Jan;20(1):17-21. doi: 10.1080/14787210.2021.1939683. Epub 2021 Jun 15. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2022. PMID: 34088250 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Recombinant Proteins for Treating Rheumatoid Arthritis.Avicenna J Med Biotechnol. 2024 Jul-Sep;16(3):137-145. doi: 10.18502/ajmb.v16i3.15739. Avicenna J Med Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39132628 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The BRIC-GARN Meeting 2011: of mice and men.Arthritis Res Ther. 2012 Feb 24;14(1):107. doi: 10.1186/ar3698. Arthritis Res Ther. 2012. PMID: 22404910 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
A pain-mediated neural signal induces relapse in murine autoimmune encephalomyelitis, a multiple sclerosis model.Elife. 2015 Aug 11;4:e08733. doi: 10.7554/eLife.08733. Elife. 2015. PMID: 26193120 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple Cytokines Elevated in Patients with Keloids: Is It an Indication of Auto-Inflammatory Disease?J Inflamm Res. 2021 Jun 10;14:2465-2470. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S312091. eCollection 2021. J Inflamm Res. 2021. PMID: 34140794 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Marrack P., Kappler J., Kotzin B. (2001) Autoimmune disease: why and where it occurs. Nat. Med. 7, 899–905 - PubMed
-
- Ermann J., Fathman C.G. (2001) Autoimmune diseases: genes, bugs and failed regulation. Nat. Immunol. 2, 759–761 - PubMed
-
- O’Shea J.J., Ma A., Lipsky P. (2002) Cytokines and autoimmunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2, 37–45 - PubMed
-
- Mathis D., Benoist C. (2004) Back to central tolerance. Immunity 20, 509–516 - PubMed
-
- Mocci S., Lafferty K., Howard M. (2000) The role of autoantigens in autoimmune disease. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 12, 725–730 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

