p53 directly transactivates Δ133p53α, regulating cell fate outcome in response to DNA damage
- PMID: 20689555
- PMCID: PMC3039296
- DOI: 10.1038/cdd.2010.91
p53 directly transactivates Δ133p53α, regulating cell fate outcome in response to DNA damage
Abstract
We have previously reported that the human p53 gene encodes at least nine different p53 isoforms, including Δ133p53α, which can modulate p53 transcriptional activity and apoptosis. In this study, we aimed to investigate the regulation of Δ133p53α isoform expression and its physiological role in modulating cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. We report here that in response to a low dose of doxorubicin (which induces cell cycle arrest without promoting apoptosis), p53 directly transactivates the human p53 internal promoter, inducing Δ133p53α protein expression. The induced Δ133p53α then inhibits p53-dependent apoptosis and G1 arrest without inhibiting p53-dependent G2 arrest. Therefore, endogenous Δ133p53α does not exclusively function in a dominant-negative manner toward p53, but differentially regulates cell cycle arrest and apoptosis.
Figures
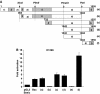

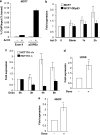
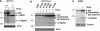
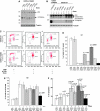

References
-
- Royds JA, Iacopetta B. p53 and disease: when the guardian angel fails. Cell Death Differ. 2006;13:1017–1026. - PubMed
-
- Braithwaite AW, Prives CL. p53: more research and more questions. Cell Death Differ. 2006;13:877–880. - PubMed
-
- Vousden KH, Lane DP. p53 in health and disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:275–283. - PubMed
-
- Lavin MF, Gueven N. The complexity of p53 stabilization and activation. Cell Death Differ. 2006;13:941–950. - PubMed
-
- Laptenko O, Prives C. Transcriptional regulation by p53: one protein, many possibilities. Cell Death Differ. 2006;13:951–961. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

