Elastic membrane that undergoes mechanical deformation enhances osteoblast cellular attachment and proliferation
- PMID: 20689620
- PMCID: PMC2905937
- DOI: 10.1155/2010/947232
Elastic membrane that undergoes mechanical deformation enhances osteoblast cellular attachment and proliferation
Abstract
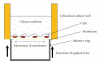
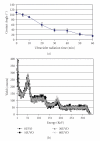
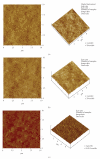
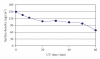
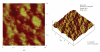
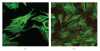
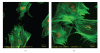
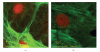
The main objective of this paper was to investigate the effect of transmission of force on bone cells that were attached to a deformable membrane. We functionalized a silastic membrane that measured 0.005 inches thickness and coated it with an extra cellular matrix (ECM) protein, fibronectin (FN). MC3T3-E1 osteoblast-like cells were cultured on the functionalized FN-coated membrane after which cell attachment and proliferation were evaluated. We observed an immediate attachment and proliferation of the bone cells on the functionalized membrane coated with FN, after 24 hours. Upon application of a mechanical force to cells cultured on the functionalized silicone membrane in the form of a dynamic equibiaxial strain, 2% magnitude; at 1-Hz frequency for 2 h, the osteoblast cells elicited slightly elevated phalloidin fluorescence, suggesting that there was reorganization of the cytoskeleton. We concluded from this preliminary data obtained that the engineered surface transduced applied mechanical forces directly to the adherent osteoblast cells via integrin binding tripeptide receptors, present in the FN molecules, resulting in the enhanced cellular attachment and proliferation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
RGD peptides immobilized on a mechanically deformable surface promote osteoblast differentiation.J Bone Miner Res. 2002 Dec;17(12):2130-40. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.2002.17.12.2130. J Bone Miner Res. 2002. PMID: 12469907
-
Sandblasting and fibronectin-derived peptide immobilization on titanium surface increase adhesion and differentiation of osteoblast-like cells (MC3T3-E1).J Dent Sci. 2016 Dec;11(4):427-436. doi: 10.1016/j.jds.2016.07.004. Epub 2016 Nov 9. J Dent Sci. 2016. PMID: 30895008 Free PMC article.
-
Transglutaminase activity arising from Factor XIIIA is required for stabilization and conversion of plasma fibronectin into matrix in osteoblast cultures.Bone. 2014 Feb;59:127-38. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2013.11.006. Epub 2013 Nov 15. Bone. 2014. PMID: 24246248
-
Fibronectin adsorption on surface-activated poly(dimethylsiloxane) and its effect on cellular function.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2004 Dec 1;71(3):449-61. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.30164. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2004. PMID: 15481053
-
Collagen Assembly at the Cell Surface: Dogmas Revisited.Cells. 2021 Mar 16;10(3):662. doi: 10.3390/cells10030662. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33809734 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Poly(Vinyl Alcohol)/Poly(Acrylic Acid) Hydrogel in a dc Electric Field: Swelling, Shape Change, and Actuation Characteristics.Int J Mater Sci. 2013;3(4):133-138. doi: 10.14355/ijmsci.2013.0304.01. Int J Mater Sci. 2013. PMID: 25478321 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of large bone defects in load-bearing bone: traditional and novel bone grafts.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2025 Apr 30;26(5):421-447. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B2300669. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2025. PMID: 40436640 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cavalcanti-Adam EA, Shapiro IM, Composto RJ, Macarak EJ, Adams CS. RGD peptides immobilized on a mechanically deformable surface promote osteoblast differentiation. Journal of Bone and Mineral Research. 2002;17(12):2130–2140. - PubMed
-
- Weyts FAA, Bosmans B, Niesing R, van Leeuwen JPTM, Weinans H. Mechanical control of human osteoblast apoptosis and proliferation in relation to differentiation. Calcified Tissue International. 2003;72(4):505–512. - PubMed
-
- Bakker AD, Soejima K, Klein-Nulend J, Burger EH. The production of nitric oxide and prostaglandin E2 by primary bone cells is shear stress dependent. Journal of Biomechanics. 2001;34(5):671–677. - PubMed
-
- Burr DB, Milgrom C, Fyhrie D, et al. In vivo measurement of human tibial strains during vigorous activity. Bone. 1996;18(5):405–410. - PubMed
-
- Turner CH, Forwood MR, Otter MW. Mechanotransduction in bone: do bone cells act as sensors of fluid flow? FASEB Journal. 1994;8(11):875–878. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

