Eltrombopag--a novel approach for the treatment of chronic immune thrombocytopenic purpura: review and safety considerations
- PMID: 20689640
- PMCID: PMC2915538
- DOI: 10.2147/dddt.s8601
Eltrombopag--a novel approach for the treatment of chronic immune thrombocytopenic purpura: review and safety considerations
Abstract
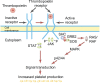
Eltrombopag is one of a number of novel agents recently developed for use in the treatment of patients with immune thrombocytopenia (ITP). Rather than preventing destruction of platelets, these agents increase the production of platelets, presumably overwhelming the immune system resulting in normal platelet counts in individuals refractory to or dependent on other therapies. These treatments are well tolerated and in randomized controlled trials show an improvement in platelet counts and a reduction in bleeding in refractory patients. This article summarizes the development of this new class of drug and evaluates the safety and efficacy of eltrombopag in patients with ITP.
Keywords: eltrombopag; immune thrombocytopenic purpura; thrombopoietin.
Figures
References
-
- Rodeghiero F, Stasi R, Gernsheimer T, et al. Standardization of terminology, definitions and outcome criteria in immune thrombocytopenic purpura of adults and children: report from an international working group. Blood. 2009;113(11):2386–2393. - PubMed
-
- McMillan R, Wang L, Tomer A, Nichol J, Pistillo J. Suppression of in vitro megakaryocyte production by antiplatelet autoantibodies from adult patients with chronic ITP. Blood. 2004;103(4):1364–1369. - PubMed
-
- Olsson B, Andersson PO, Jernas M, et al. T-cell-mediated cytotoxicity toward platelets in chronic idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Nat Med. 2003;9(9):1123–1124. - PubMed
-
- Gernsheimer T, Stratton J, Ballem PJ, Slichter SJ. Mechanisms of response to treatment in autoimmune thrombocytopenic purpura. N Engl J Med. 1989;320(15):974–980. - PubMed
-
- Houwerzijl EJ, Blom NR, van der Want JJ, Vellenga E, de Wolf JT. Megakaryocytic dysfunction in myelodysplastic syndromes and idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura is in part due to different forms of cell death. Leukemia. 2006;20(11):1937–1942. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

