The glycobiome of the rumen bacterium Butyrivibrio proteoclasticus B316(T) highlights adaptation to a polysaccharide-rich environment
- PMID: 20689770
- PMCID: PMC2914790
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0011942
The glycobiome of the rumen bacterium Butyrivibrio proteoclasticus B316(T) highlights adaptation to a polysaccharide-rich environment
Abstract
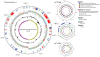
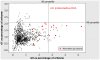
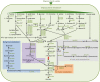
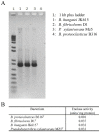
Determining the role of rumen microbes and their enzymes in plant polysaccharide breakdown is fundamental to understanding digestion and maximising productivity in ruminant animals. Butyrivibrio proteoclasticus B316(T) is a gram-positive, butyrate-forming rumen bacterium with a key role in plant polysaccharide degradation. The 4.4 Mb genome consists of 4 replicons; a chromosome, a chromid and two megaplasmids. The chromid is the smallest reported for all bacteria, and the first identified from the phylum Firmicutes. B316 devotes a large proportion of its genome to the breakdown and reassembly of complex polysaccharides and has a highly developed glycobiome when compared to other sequenced bacteria. The secretion of a range of polysaccharide-degrading enzymes which initiate the breakdown of pectin, starch and xylan, a subtilisin family protease active against plant proteins, and diverse intracellular enzymes to break down oligosaccharides constitute the degradative capability of this organism. A prominent feature of the genome is the presence of multiple gene clusters predicted to be involved in polysaccharide biosynthesis. Metabolic reconstruction reveals the absence of an identifiable gene for enolase, a conserved enzyme of the glycolytic pathway. To our knowledge this is the first report of an organism lacking an enolase. Our analysis of the B316 genome shows how one organism can contribute to the multi-organism complex that rapidly breaks down plant material in the rumen. It can be concluded that B316, and similar organisms with broad polysaccharide-degrading capability, are well suited to being early colonizers and degraders of plant polysaccharides in the rumen environment.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Butyrivibrio hungatei MB2003 Competes Effectively for Soluble Sugars Released by Butyrivibrio proteoclasticus B316T during Growth on Xylan or Pectin.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2019 Jan 23;85(3):e02056-18. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02056-18. Print 2019 Feb 1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30478228 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Genomics of Rumen Butyrivibrio spp. Uncovers a Continuum of Polysaccharide-Degrading Capabilities.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2019 Dec 13;86(1):e01993-19. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01993-19. Print 2019 Dec 13. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31653790 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular polysaccharide-degrading proteome of Butyrivibrio proteoclasticus.J Proteome Res. 2012 Jan 1;11(1):131-42. doi: 10.1021/pr200864j. Epub 2011 Nov 29. J Proteome Res. 2012. PMID: 22060546
-
Lignocellulose degradation by rumen bacterial communities: New insights from metagenome analyses.Environ Res. 2023 Jul 15;229:115925. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2023.115925. Epub 2023 Apr 21. Environ Res. 2023. PMID: 37086884 Review.
-
Polysaccharide utilization by gut bacteria: potential for new insights from genomic analysis.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2008 Feb;6(2):121-31. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro1817. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18180751 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring the microbial diversity and characterization of cellulase and hemicellulase genes in goat rumen: a metagenomic approach.BMC Biotechnol. 2023 Dec 4;23(1):51. doi: 10.1186/s12896-023-00821-6. BMC Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 38049781 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary energy and protein levels influenced the growth performance, ruminal morphology and fermentation and microbial diversity of lambs.Sci Rep. 2019 Nov 12;9(1):16612. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-53279-y. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31719633 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the bovine rumen microbiome reveals a diversity of Sus-like polysaccharide utilization loci from the bacterial phylum Bacteroidetes.J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2014 Mar;41(3):601-6. doi: 10.1007/s10295-013-1395-y. Epub 2014 Jan 22. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2014. PMID: 24448980
-
Rumen bacterial community structure impacts feed efficiency in beef cattle.J Anim Sci. 2018 Apr 3;96(3):1045-1058. doi: 10.1093/jas/skx081. J Anim Sci. 2018. PMID: 29617864 Free PMC article.
-
Evolving understanding of rumen methanogen ecophysiology.Front Microbiol. 2023 Nov 6;14:1296008. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1296008. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 38029083 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cosgrove DJ. Growth of the plant cell wall. Nat Rev Mol Cell Bio. 2005;6:850–861. - PubMed
-
- Flint HJ, Bayer EA, Rincon MT, Lamed R, White BA. Polysaccharide utilization by gut bacteria: potential for new insights from genomic analysis. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2008;6:121–131. - PubMed
-
- Edwards JE, McEwan NR, Travis AJ, Wallace RJ. 16S rRNA library-based analysis of ruminal bacterial diversity. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek. 2004;86:263–282. - PubMed
-
- Edwards JE, Huws SA, Kim EJ, Kingston-Smith AH. Characterization of the dynamics of initial bacterial colonization of nonconserved forage in the bovine rumen. FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2007;62:323–335. - PubMed
-
- Koike S, Yoshitani S, Kobayashi Y, Tanaka K. Phylogenetic analysis of fiber-associated rumen bacterial community and PCR detection of uncultured bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2003;229:23–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

