In vitro effects of imatinib mesylate on radiosensitivity and chemosensitivity of breast cancer cells
- PMID: 20691121
- PMCID: PMC2925350
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-412
In vitro effects of imatinib mesylate on radiosensitivity and chemosensitivity of breast cancer cells
Abstract
Background: Breast cancer treatment is based on a combination of adjuvant chemotherapy followed by radiotherapy effecting intracellular signal transduction. With the tyrosine kinase inhibitors new targeted drugs are available. Imatinib mesylate is a selective inhibitor of bcr-abl, PRGFR alpha, beta and c-kit. The purpose of this study was to determine whether Imatinib has an influence on the effectiveness of radiotherapy in breast cancer cell lines and if a combination of imatinib with standard chemotherapy could lead to increased cytoreduction.
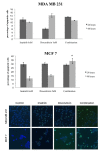
Methods: Colony-forming tests of MCF 7 and MDA MB 231 were used to study differences in cell proliferation under incubation with imatinib and radiation. Changes in expression and phosphorylation of target receptors were detected using western blot. Cell proliferation, migration and apoptosis assays were performed combining imatinib with doxorubicin.
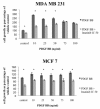
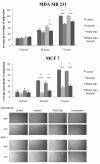
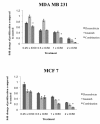
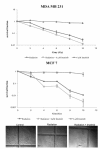
Results: The combination of imatinib and radiotherapy showed a significantly stronger inhibition of cell proliferation compared to single radiotherapy. Differences in PDGFR expression could not be detected, but receptor phosphorylation was significantly inhibited when treated with imatinib. Combination of imatinib with standard chemotherapy lead to an additive effect on cell growth inhibition compared to single treatment.
Conclusions: Imatinib treatment combined with radiotherapy leads in breast cancer cell lines to a significant benefit which might be influenced through inhibition of PDGFR phosphorylation. Combining imatinib with chemotherapy enhances cytoreductive effects. Further in vivo studies are needed to evaluate the benefit of Imatinib in combination with radiotherapy and chemotherapy on the treatment of breast cancer.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Novel treatment of ovarian cancer cell lines with Imatinib mesylate combined with Paclitaxel and Carboplatin leads to receptor-mediated antiproliferative effects.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2008 Dec;134(12):1397-405. doi: 10.1007/s00432-008-0408-0. Epub 2008 May 9. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2008. PMID: 18465140 Free PMC article.
-
Combination of imatinib and vinorelbine enhances cell growth inhibition in breast cancer cells via PDGFR beta signalling.Cancer Lett. 2009 Jan 8;273(1):70-9. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2008.07.040. Epub 2008 Sep 21. Cancer Lett. 2009. PMID: 18809244
-
Effect of imatinib mesylate on neuroblastoma tumorigenesis and vascular endothelial growth factor expression.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2004 Jan 7;96(1):46-55. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djh004. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2004. PMID: 14709738
-
Use and limitations of imatinib mesylate (Glivec), a selective inhibitor of the tyrosine kinase Abl transcript in the treatment of chronic myeloid leukaemia.Br J Biomed Sci. 2004;61(2):103-11. doi: 10.1080/09674845.2004.11732653. Br J Biomed Sci. 2004. PMID: 15250677 Review.
-
Imatinib mesylate: in the treatment of gastrointestinal stromal tumours.Drugs. 2003;63(5):513-22; discussion 523-4. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200363050-00005. Drugs. 2003. PMID: 12600228 Review.
Cited by
-
Malignant stroma increases luminal breast cancer cell proliferation and angiogenesis through platelet-derived growth factor signaling.BMC Cancer. 2014 Oct 1;14:735. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-14-735. BMC Cancer. 2014. PMID: 25274034 Free PMC article.
-
Doxorubicin induces atypical NF-κB activation through c-Abl kinase activity in breast cancer cells.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2013 Oct;139(10):1625-35. doi: 10.1007/s00432-013-1476-3. Epub 2013 Jul 28. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23892407 Free PMC article.
-
Digital microfluidic immunocytochemistry in single cells.Nat Commun. 2015 Jun 24;6:7513. doi: 10.1038/ncomms8513. Nat Commun. 2015. PMID: 26104298 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the PDGF signaling pathway in tumor treatment.Cell Commun Signal. 2013 Dec 20;11:97. doi: 10.1186/1478-811X-11-97. Cell Commun Signal. 2013. PMID: 24359404 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of proliferation and migration of luminal and claudin-low breast cancer cells by PDGFR inhibitors.Cancer Cell Int. 2014 Sep 5;14(1):89. doi: 10.1186/s12935-014-0089-5. eCollection 2014. Cancer Cell Int. 2014. PMID: 25253994 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Niehoff P. Breast irradiation with brachytherapy: approved techniques and new concepts. Minerva Ginecol. 2007;59(4):377–86. - PubMed
-
- Fong TA. SU5416 is a potent and selective inhibitor of the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (Flk-1/KDR) that inhibits tyrosine kinase catalysis, tumor vascularization, and growth of multiple tumor types. Cancer Res. 1999;59(1):99–106. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

