Tea catechins as inhibitors of receptor tyrosine kinases: mechanistic insights and human relevance
- PMID: 20691268
- PMCID: PMC2974766
- DOI: 10.1016/j.phrs.2010.07.010
Tea catechins as inhibitors of receptor tyrosine kinases: mechanistic insights and human relevance
Abstract
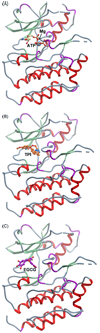
Receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) play important roles in the control of fundamental cellular processes, influencing the balance between cell proliferation and death. RTKs have emerged as molecular targets for the treatment of various cancers. Green tea and its polyphenolic compounds, the catechins, exhibit chemopreventive and chemotherapeutic properties in many human cancer cell types, as well as in various carcinogenicity models in vivo. Epidemiological studies are somewhat less convincing, but some positive correlations have been observed. The tea catechins, including (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG), have pleiotropic effects on cellular proteins and signaling pathways. This review focuses on the ability of the tea constituents to suppress RTK signaling, and summarizes the mechanisms by which EGCG and other catechins might exert their protective effects towards dysregulated RTKs in cancer cells. The findings are discussed in the context of ongoing clinical trials with RTK inhibitors, and the possibility for drug/nutrient interactions enhancing therapeutic efficacy.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cancer chemoprevention with green tea catechins by targeting receptor tyrosine kinases.Mol Nutr Food Res. 2011 Jun;55(6):832-43. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201000622. Epub 2011 May 2. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2011. PMID: 21538846 Review.
-
Targeting receptor tyrosine kinases for chemoprevention by green tea catechin, EGCG.Int J Mol Sci. 2008 Jun;9(6):1034-1049. doi: 10.3390/ijms9061034. Epub 2008 Jun 20. Int J Mol Sci. 2008. PMID: 19325845 Free PMC article.
-
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG): chemical and biomedical perspectives.Phytochemistry. 2006 Sep;67(17):1849-55. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2006.06.020. Epub 2006 Jul 31. Phytochemistry. 2006. PMID: 16876833 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting multiple signaling pathways by green tea polyphenol (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate.Cancer Res. 2006 Mar 1;66(5):2500-5. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-3636. Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 16510563 Review.
-
Reading the tea leaves: anticarcinogenic properties of (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate.Mayo Clin Proc. 2007 Jun;82(6):725-32. doi: 10.4065/82.6.725. Mayo Clin Proc. 2007. PMID: 17550753 Review.
Cited by
-
Hemp Seeds in Post-Arthroplasty Rehabilitation: A Pilot Clinical Study and an In Vitro Investigation.Nutrients. 2021 Nov 30;13(12):4330. doi: 10.3390/nu13124330. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34959882 Free PMC article.
-
Green Tea Catechins for Prostate Cancer Prevention: Present Achievements and Future Challenges.Antioxidants (Basel). 2017 Apr 5;6(2):26. doi: 10.3390/antiox6020026. Antioxidants (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28379200 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PARP-1-Associated Pathological Processes: Inhibition by Natural Polyphenols.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 23;22(21):11441. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111441. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34768872 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The interplay of exercise and green tea: a new road in cancer therapy.Cancer Cell Int. 2025 Jan 7;25(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s12935-024-03632-7. Cancer Cell Int. 2025. PMID: 39773739 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endothelins and their receptors in cancer: identification of therapeutic targets.Pharmacol Res. 2011 Jun;63(6):519-24. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2011.01.002. Epub 2011 Jan 18. Pharmacol Res. 2011. PMID: 21251982 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ferruzzi MG. The influence of beverage composition on delivery of phenolic compounds from coffee and tea. Physiol Behav. 2010;100:33–41. - PubMed
-
- Higdon JV, Frei B. Tea catechins and polyphenols: health effects, metabolism, and antioxidant functions. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2003;43:89–143. - PubMed
-
- Wang Y, Ho CT. Polyphenolic chemistry of tea and coffee: a century of progress. J Agric Food Chem. 2009;57:8109–8114. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources