Delivery of chlorambucil using an acoustically-triggered perfluoropentane emulsion
- PMID: 20691925
- PMCID: PMC2933659
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2010.04.019
Delivery of chlorambucil using an acoustically-triggered perfluoropentane emulsion
Abstract
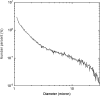
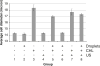
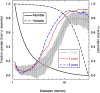
Ultrasound-mediated delivery systems have mainly focused on microbubble contrast agents as carriers of drugs or genetic material. This study uses micron-sized, perfluoropentane (PFP) emulsions as carriers of chlorambucil (CHL), a lipophilic chemotherapeutic. The release of CHL is achieved via acoustic droplet vaporization (ADV), whereby the superheated emulsion is converted into gas bubbles using ultrasound. Emulsions were made using an albumin shell and soybean oil as the CHL carrier. The ratio of the PFP to soybean oil phases in the droplets and the fraction of droplets that vaporize per ultrasound exposure were shown to correlate with droplet diameter. A 60-min incubation with the CHL-loaded emulsion caused a 46.7% cellular growth inhibition, whereas incubation with the CHL-loaded emulsion that was exposed to ultrasound at 6.3 MHz caused an 84.3% growth inhibition. This difference was statistically significant (p < 0.01), signifying that ADV can be used as a method to substantially enhance drug delivery.
Copyright 2010 World Federation for Ultrasound in Medicine & Biology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Delivery of water-soluble drugs using acoustically triggered perfluorocarbon double emulsions.Pharm Res. 2010 Dec;27(12):2753-65. doi: 10.1007/s11095-010-0277-5. Epub 2010 Sep 25. Pharm Res. 2010. PMID: 20872050 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrafast dynamics of the acoustic vaporization of phase-change microdroplets.J Acoust Soc Am. 2013 Aug;134(2):1610-21. doi: 10.1121/1.4812882. J Acoust Soc Am. 2013. PMID: 23927201
-
Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of chlorambucil delivered in parenteral emulsion.Int J Pharm. 2008 Aug 6;360(1-2):115-21. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2008.04.027. Epub 2008 Apr 22. Int J Pharm. 2008. PMID: 18508212
-
Nanobubbles: a promising efficient tool for therapeutic delivery.Ther Deliv. 2016;7(2):117-38. doi: 10.4155/tde.15.92. Epub 2016 Jan 15. Ther Deliv. 2016. PMID: 26769397 Review.
-
Acoustic droplet vaporization in biology and medicine.Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:404361. doi: 10.1155/2013/404361. Epub 2013 Nov 20. Biomed Res Int. 2013. PMID: 24350267 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Acoustic droplet-hydrogel composites for spatial and temporal control of growth factor delivery and scaffold stiffness.Acta Biomater. 2013 Jul;9(7):7399-409. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2013.03.027. Epub 2013 Mar 25. Acta Biomater. 2013. PMID: 23535233 Free PMC article.
-
Noninvasive Ultrasonic Drug Uncaging Maps Whole-Brain Functional Networks.Neuron. 2018 Nov 7;100(3):728-738.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2018.10.042. Neuron. 2018. PMID: 30408444 Free PMC article.
-
Scavenging dissolved oxygen via acoustic droplet vaporization.Ultrason Sonochem. 2016 Jul;31:394-403. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2016.01.019. Epub 2016 Jan 19. Ultrason Sonochem. 2016. PMID: 26964964 Free PMC article.
-
Laser irradiated fluorescent perfluorocarbon microparticles in 2-D and 3-D breast cancer cell models.Sci Rep. 2017 Mar 6;7:43408. doi: 10.1038/srep43408. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28262671 Free PMC article.
-
Applications of Ultrasound to Stimulate Therapeutic Revascularization.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jun 24;20(12):3081. doi: 10.3390/ijms20123081. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31238531 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Apfel RE. Activatable infusable dispersions containing drops of a superheated liquid for methods of therapy and diagnosis. Patent 5,840,276. 1998.
-
- Borden MA, Caskey CF, Little E, Gillies RJ, Ferrara KW. DNA and polylysine adsorption and multilayer construction onto cationic lipid-coated microbubbles. Langmuir. 2007;23(18):9401–9408. - PubMed
-
- Bucala R, Kawakami M, Cerami A. Cytotoxicity of a perfluorocarbon blood substitute to macrophages in vitro. Science. 1983;220(4600):965–967. - PubMed
-
- Centis V, Doillon CJ, Vermette P. Perfluorocarbon emulsions cytotoxic effects on human fibroblasts and effect of aging on particle size distribution. Artif Organs. 2007;31(8):649–653. - PubMed
-
- Dalecki D. Mechanical bioeffects of ultrasound. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2004;6(1):229–248. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

