Psoriasis genetics: breaking the barrier
- PMID: 20692714
- PMCID: PMC2957827
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tig.2010.06.006
Psoriasis genetics: breaking the barrier
Abstract
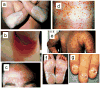
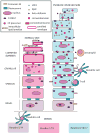
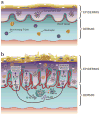
Psoriasis is a common incurable inflammatory skin disease affecting 2-3% of the European population. Psoriatic skin contains large numbers of immune cells which produce many cytokines, chemokines and inflammatory molecules. The epidermis divides much faster than normal and has a defective outer layer or barrier which under normal circumstances protects from infection and dehydration. Psoriatic skin is characterized by a distinct set of inflammation and epidermal proliferation and differentiation markers, and it has been unclear whether the genetic basis of psoriasis reflects defects of the immune system or of the skin. One genetic determinant lies within the major histocompatibility complex class 1 region. Genome-wide association studies have revealed genetic susceptibility factors that play a role in the formation of immune cells found in psoriasis lesions. Others affect epidermal proliferation and skin barrier formation. Hence, genetic components of both the immune system and the epidermis can predispose to disease.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Bhalerao J, Bowcock A. The genetics of psoriasis: a complex disorder of the skin and immune system. Hum Mol Genet. 1998;7:1537–1545. - PubMed
-
- Arnett FC, et al. Psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis associated with human immunodeficiency virus infection. Rheumatic Diseases Clinics of North America. 1991;17:59–78. - PubMed
-
- Rongioletti F, et al. Psoriasis Induced or Aggravated by Drugs. The Journal of Rheumatology. 2009;83:59–61. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

