Measurement of islet cell antibodies in the Type 1 Diabetes Genetics Consortium: efforts to harmonize procedures among the laboratories
- PMID: 20693189
- PMCID: PMC2917851
- DOI: 10.1177/1740774510373496
Measurement of islet cell antibodies in the Type 1 Diabetes Genetics Consortium: efforts to harmonize procedures among the laboratories
Abstract
Background: and
Purpose: Three network laboratories measured antibodies to islet autoantigens. Antibodies to glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD65 [GADA]) and the intracellular portion of protein tyrosine phosphatase (IA-2(ic) [IA-2A]) were measured by similar, but not identical, methods in samples from participants in the Type 1 Diabetes Genetics Consortium (T1DGC).
Methods: All laboratories used radiobinding assays to detect antibodies to in vitro transcribed and translated antigen, but with different local standards, calibrated against the World Health Organization (WHO) reference reagent. Using a common method to calculate WHO units/mL, we compared results reported on samples included in the Diabetes Autoantibody Standardization Program (DASP), and developed standard methods for reporting in WHO units/mL. We evaluated intra-assay and inter-assay coefficient of variation (CV) in blind duplicate samples and assay comparability in four DASP workshops.
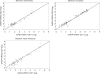
Results: Values were linearly related in the three laboratories for both GADA and IA-2A, and intra-assay technical errors for values within the standard curve were below 13% for GADA and below 8.5% for IA-2A. Correlations in samples tested 1-2 years apart were >97%. Over the course of the study, internal CVs were 10-20% with one exception, and the laboratories concordantly called samples GADA or IA-2A positive or negative in 96.7% and 99.6% of duplicates within the standard curve. Despite acceptable CVs and general concordance in ranking samples, the laboratories differed markedly in absolute values for GADA and IA-2A reported in WHO units/mL in DASP over a large range of values.
Limitations: With three laboratories using different assay methods (including calibrators), consistent values among them could not be attained.
Conclusions: Modifications in the assays are needed to improve comparability of results expressed as WHO units/mL across laboratories. It will be essential to retain high intra- and inter-assay precision, sensitivity and specificity and to confirm the accuracy of harmonized methods.
Figures



References
-
- Baekkeskov S, Aanstoot HJ, Christgau S, et al. Identification of the 64K autoantigen in insulin-dependent diabetes as GABA-synthesizing enzyme glutamic acid decarboxylase. Nature(London: )1990; 347: 151–56 - PubMed
-
- Rabin DU, Pleasic SM, Shapiro JA, et al. Islet cell antigen 512 is a diabetes-specific islet autoantigen related to protein tyrosine phosphatases. J Immunol 1994; 152: 3183–88 - PubMed
-
- Lan SM, Lu J, Goto Y, Notkins AJ. Molecular cloning and identification of a receptor-type protein tyrosine phosphatase, IA-2, from human insulinoma. DNA Cell Biol 1994; 13: 505–14 - PubMed
-
- Bonifacio E, Genovese S, Braghi S, et al. Islet autoantibody markers in IDDM: risk assessment strategies yielding high sensitivity. Diabetologia 1995; 38: 816–22 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

