Determination of odor detection threshold in the Gottingen minipig
- PMID: 20693277
- PMCID: PMC2943411
- DOI: 10.1093/chemse/bjq076
Determination of odor detection threshold in the Gottingen minipig
Abstract
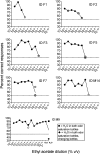
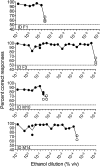
The aim of the study was to examine the ability of Göttingen minipigs to acquire an olfaction-based operant conditioning task and to determine the detection threshold for ethyl acetate and ethanol. We used an automated olfactometer developed for rodents to train and test 14 pigs. Odor sampling and reliable responding were obtained after three to fifteen 160-trial sessions. Successful transfer of the task from ethyl acetate to ethanol was achieved in 1-4 sessions. Detection threshold for ethyl acetate varied between 10(-2)% and 10(-6)% v/v and for ethanol between 0.1% and 5 × 10(-6)% v/v. The results provide evidence that minipigs can successfully acquire 2-odorant discrimination using a food-rewarded instrumental conditioning paradigm for testing olfactory function. This olfactory discrimination paradigm provides reliable measures of olfactory sensitivity and thereby enables detection of changes in olfaction in a porcine model of Alzheimer's disease currently being developed.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Performance of mice in an automated olfactometer: odor detection, discrimination and odor memory.Chem Senses. 1999 Dec;24(6):637-45. doi: 10.1093/chemse/24.6.637. Chem Senses. 1999. PMID: 10587496
-
Influence of adrenalectomy on the odor detection performance of rats.Physiol Behav. 1991 Jun;49(6):1273-7. doi: 10.1016/0031-9384(91)90362-r. Physiol Behav. 1991. PMID: 1896510
-
Characterizing olfactory binary mixture interactions in Fischer 344 rats using behavioral reaction times.Chem Senses. 2015 Jun;40(5):325-34. doi: 10.1093/chemse/bjv014. Epub 2015 Apr 15. Chem Senses. 2015. PMID: 25877697 Free PMC article.
-
The perception of odor is not a surrogate marker for chemical exposure: a review of factors influencing human odor perception.Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2013 Feb;51(2):70-6. doi: 10.3109/15563650.2013.767908. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2013. PMID: 23387344 Review.
-
An odor is not worth a thousand words: from multidimensional odors to unidimensional odor objects.Annu Rev Psychol. 2010;61:219-41, C1-5. doi: 10.1146/annurev.psych.60.110707.163639. Annu Rev Psychol. 2010. PMID: 19958179 Review.
Cited by
-
The Pig Olfactory Brain: A Primer.Chem Senses. 2016 Jun;41(5):415-25. doi: 10.1093/chemse/bjw016. Epub 2016 Mar 2. Chem Senses. 2016. PMID: 26936231 Free PMC article.
-
Odor exploration behavior of the domestic pig (Sus scrofa) as indicator of enriching properties of odors.Front Behav Neurosci. 2023 May 5;17:1173298. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2023.1173298. eCollection 2023. Front Behav Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37214639 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arave CW. Assessing sensory capacity of animals using operant technology. J Anim Sci. 1996;74:1996–2009. - PubMed
-
- Attems J, Lintner F, Jellinger KA. Olfactory involvement in aging and Alzheimer's disease: an autopsy study. J Alzheimers Dis. 2005;7:149–157. - PubMed
-
- Bodyak N, Slotnick B. Performance of mice in an automated olfactometer: odor detection, discrimination and odor memory. Chem Senses. 1999;24:637–645. - PubMed
-
- Cometto-Muniz JE, Cain WS. Nasal pungency, odor, and eye irritation thresholds for homologous acetates. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1991;39:983–989. - PubMed
-
- Cometto-Muniz JE, Cain WS, Abraham MH. Quantification of chemical vapors in chemosensory research. Chem Senses. 2003;28:467–477. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

