Expression of store-operated Ca2+ entry and transient receptor potential canonical and vanilloid-related proteins in rat distal pulmonary venous smooth muscle
- PMID: 20693314
- PMCID: PMC2980387
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00176.2009
Expression of store-operated Ca2+ entry and transient receptor potential canonical and vanilloid-related proteins in rat distal pulmonary venous smooth muscle
Abstract
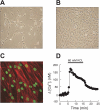
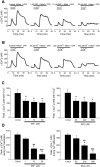
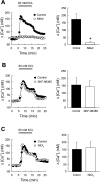
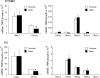
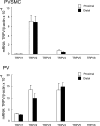
Chronic hypoxia causes remodeling and alters contractile responses in both pulmonary arteries and pulmonary veins. Although pulmonary arteries have been studied extensively in these disorders, the mechanisms by which pulmonary veins respond to hypoxia and whether these responses contribute to chronic hypoxic pulmonary hypertension remain poorly understood. In pulmonary arterial smooth muscle, we have previously demonstrated that influx of Ca(2+) through store-operated calcium channels (SOCC) thought to be composed of transient receptor potential (TRP) proteins is likely to play an important role in development of chronic hypoxic pulmonary hypertension. To determine whether this mechanism could also be operative in pulmonary venous smooth muscle, we measured intracellular Ca(2+) concentration ([Ca(2+)](i)) by fura-2 fluorescence microscopy in primary cultures of pulmonary venous smooth muscle cells (PVSMC) isolated from rat distal pulmonary veins. In cells perfused with Ca(2+)-free media containing cyclopiazonic acid (10 μM) and nifedipine (5 μM) to deplete sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+) stores and block voltage-dependent Ca(2+) channels, restoration of extracellular Ca(2+) (2.5 mM) caused marked increases in [Ca(2+)](i), whereas MnCl(2) (200 μM) quenched fura-2 fluorescence, indicating store-operated Ca(2+) entry (SOCE). SKF-96365 and NiCl(2), antagonists of SOCC, blocked SOCE at concentrations that did not alter Ca(2+) responses to 60 mM KCl. Of the seven known canonical TRP (TRPC1-7) and six vanilloid-related TRP channels (TRPV1-6), real-time PCR revealed mRNA expression of TRPC1 > TRPC6 > TRPC4 > TRPC2 ≈ TRPC5 > TRPC3, TRPV2 > TRPV4 > TRPV1 in distal PVSMC, and TRPC1 > TRPC6 > TRPC3 > TRPC4 ≈ TRPC5, TRPV2 ≈ TRPV4 > TRPV1 in rat distal pulmonary vein (PV) smooth muscle. Western blotting confirmed protein expression of TRPC1, TRPC6, TRPV2, and TRPV4 in both PVSMC and PV. Our results suggest that SOCE through Ca(2+) channels composed of TRP proteins may contribute to Ca(2+) signaling in rat distal PV smooth muscle.
Figures
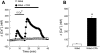
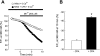
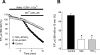
Similar articles
-
Differences in STIM1 and TRPC expression in proximal and distal pulmonary arterial smooth muscle are associated with differences in Ca2+ responses to hypoxia.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2008 Jul;295(1):L104-13. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00058.2008. Epub 2008 Apr 18. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18424621 Free PMC article.
-
Bone morphogenetic protein 4 enhances canonical transient receptor potential expression, store-operated Ca2+ entry, and basal [Ca2+]i in rat distal pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2010 Dec;299(6):C1370-8. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00040.2010. Epub 2010 Sep 15. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20844246 Free PMC article.
-
Capacitative calcium entry and TRPC channel proteins are expressed in rat distal pulmonary arterial smooth muscle.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2004 Apr;286(4):L848-58. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00319.2003. Epub 2003 Dec 12. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2004. PMID: 14672922
-
Physiological functions of transient receptor potential channels in pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010;661:109-22. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60761-500-2_7. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010. PMID: 20204726 Review.
-
TRPC channels in smooth muscle cells.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2010 Jun 1;15(3):1023-39. doi: 10.2741/3660. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2010. PMID: 20515740 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
"TRPV1 is a component of the atrial natriuretic signaling complex, and using orally delivered antagonists, presents a valid therapeutic target in the longitudinal reversal and treatment of cardiac hypertrophy and heart failure".Channels (Austin). 2019 Dec;13(1):1-16. doi: 10.1080/19336950.2018.1547611. Channels (Austin). 2019. PMID: 30424709 Free PMC article.
-
Tyrosine phosphorylation tunes chemical and thermal sensitivity of TRPV2 ion channel.Elife. 2022 Jun 10;11:e78301. doi: 10.7554/eLife.78301. Elife. 2022. PMID: 35686730 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenic role of store-operated and receptor-operated ca(2+) channels in pulmonary arterial hypertension.J Signal Transduct. 2012;2012:951497. doi: 10.1155/2012/951497. Epub 2012 Sep 27. J Signal Transduct. 2012. PMID: 23056939 Free PMC article.
-
Distribution and Assembly of TRP Ion Channels.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1349:111-138. doi: 10.1007/978-981-16-4254-8_7. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 35138613
-
Acute hypoxia activates store-operated Ca(2+) entry and increases intracellular Ca(2+) concentration in rat distal pulmonary venous smooth muscle cells.J Thorac Dis. 2013 Oct;5(5):605-12. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2072-1439.2013.08.68. J Thorac Dis. 2013. PMID: 24255773 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abed E, Labelle D, Martineau C, Loghin A, Moreau R. Expression of transient receptor potential (TRP) channels in human and murine osteoblast-like cells. Mol Membr Biol 26: 146–158, 2009 - PubMed
-
- Aharinejad S, Schraufnagel DE, Miksovsky A, Larson EK, Marks SC., Jr Endothelin-1 focally constricts pulmonary veins in rats. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 110: 148–156, 1995 - PubMed
-
- Brink C, Gillard V, Roubert P, Mencia-Huerta JM, Chabrier PE, Braquet P, Verley J. Effects and specific binding sites of endothelin in human lung preparations. Pulm Pharmacol 4: 54–59, 1991 - PubMed
-
- Bronquard C, Maupoil V, Arbeille B, Fetissof F, Findlay I, Cosnay P, Freslon JL. Contractile and relaxant properties of rat-isolated pulmonary veins related to localization and histology. Fundam Clin Pharmacol 21: 55–65, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Gao Y, Raj JU. Role of veins in regulation of pulmonary circulation. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 288: L213–L226, 2005 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

