A subset of epithelial cells with CCSP promoter activity participates in alveolar development
- PMID: 20693404
- PMCID: PMC3135842
- DOI: 10.1165/rcmb.2009-0429OC
A subset of epithelial cells with CCSP promoter activity participates in alveolar development
Abstract
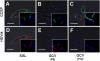
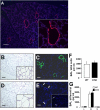
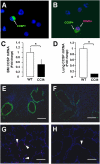
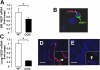
Alveolar formation is hallmarked by the transition of distal lung saccules into gas exchange units through the emergence of secondary crests and an exponential increase in surface area. Several cell types are involved in this complex process, including families of epithelial cells that differentiate into alveolar type I and II cells. Subsets of cells expressing Clara cell secretory protein (CCSP) have been identified in both lung and bone marrow compartments, and are described as a progenitor/stem cell pool involved in airway regeneration and alveolar homeostasis. Whether these cells also participate in alveolar formation during postnatal development remains unknown. Based on their regenerative capacity, we asked whether these cells participate in alveogenesis. We used a previously described transgenic mouse model (CCSP-tk) in which Ganciclovir exposure selectively depletes all cells with CCSP promoter activity through intracellular generation of a toxic metabolite of thymidine kinase. Our results showed that Ganciclovir treatment in newborn CCtk mice depleted this cell population in lung airways and bone marrow, and was associated with alveolar hypoplasia and respiratory failure. Hypoplastic lungs had fewer alveolar type I and II cells, with impaired secondary crest formation and decreased vascular endothelial growth factor expression in distal airways. These findings are consistent with a model in which a unique population of cells with CCSP promoter activity that expresses vascular endothelial growth factor participates in alveolar development.
Figures

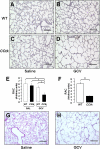

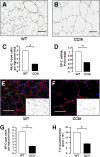
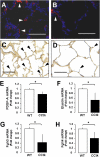
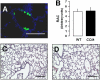
References
-
- Galambos C, Demello DE. Regulation of alveologenesis: clinical implications of impaired growth. Pathology 2008;40:124–140. - PubMed
-
- Husain AN, Siddiqui NH, Stocker JT. Pathology of arrested acinar development in postsurfactant bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Hum Pathol 1998;29:710–717. - PubMed
-
- Jobe AJ. The new BPD: an arrest of lung development. Pediatr Res 1999;46:641–643. - PubMed
-
- Stripp BR, Maxson K, Mera R, Singh G. Plasticity of airway cell proliferation and gene expression after acute naphthalene injury. Am J Physiol 1995;269:L791–L799. - PubMed
-
- Reynolds SD, Hong KU, Giangreco A, Mango GW, Guron C, Morimoto Y, Stripp BR. Conditional Clara cell ablation reveals a self-renewing progenitor function of pulmonary neuroendocrine cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2000;278:L1256–L1263. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

