Heterologous expression and extracellular secretion of cellulolytic enzymes by Zymomonas mobilis
- PMID: 20693448
- PMCID: PMC2950452
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.00230-10
Heterologous expression and extracellular secretion of cellulolytic enzymes by Zymomonas mobilis
Abstract
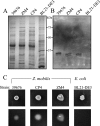
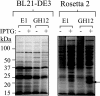
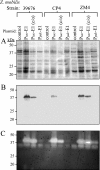
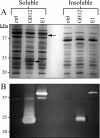
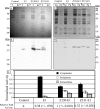
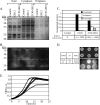
Development of the strategy known as consolidated bioprocessing (CBP) involves the use of a single microorganism to convert pretreated lignocellulosic biomass to ethanol through the simultaneous production of saccharolytic enzymes and fermentation of the liberated monomeric sugars. In this report, the initial steps toward achieving this goal in the fermentation host Zymomonas mobilis were investigated by expressing heterologous cellulases and subsequently examining the potential to secrete these cellulases extracellularly. Numerous strains of Z. mobilis were found to possess endogenous extracellular activities against carboxymethyl cellulose, suggesting that this microorganism may harbor a favorable environment for the production of additional cellulolytic enzymes. The heterologous expression of two cellulolytic enzymes, E1 and GH12 from Acidothermus cellulolyticus, was examined. Both proteins were successfully expressed as soluble, active enzymes in Z. mobilis although to different levels. While the E1 enzyme was less abundantly expressed, the GH12 enzyme comprised as much as 4.6% of the total cell protein. Additionally, fusing predicted secretion signals native to Z. mobilis to the N termini of E1 and GH12 was found to direct the extracellular secretion of significant levels of active E1 and GH12 enzymes. The subcellular localization of the intracellular pools of cellulases revealed that a significant portion of both the E1 and GH12 secretion constructs resided in the periplasmic space. Our results strongly suggest that Z. mobilis is capable of supporting the expression and secretion of high levels of cellulases relevant to biofuel production, thereby serving as a foundation for developing Z. mobilis into a CBP platform organism.
Figures
References
-
- Arnold, K., L. Bordoli, J. Kopp, and T. Schwede. 2006. The SWISS-MODEL workspace: a web-based environment for protein structure homology modelling. Bioinformatics 22:195-201. - PubMed
-
- Bendtsen, J. D., H. Nielsen, G. von Heijne, and S. Brunak. 2004. Improved prediction of signal peptides: SignalP 3.0. J. Mol. Biol. 340:783-795. - PubMed
-
- Brestic-Goachet, N., P. Gunasekaran, B. Cami, and J. Baratti. 1990. Transfer and expression of a Bacillus licheniformis alpha-amylase gene in Zymomonas mobilis. Arch. Microbiol. 153:219-225.
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

