G protein-coupled receptor-associated sorting protein 1 regulates the postendocytic sorting of seven-transmembrane-spanning G protein-coupled receptors
- PMID: 20693822
- PMCID: PMC2919430
- DOI: 10.1159/000314161
G protein-coupled receptor-associated sorting protein 1 regulates the postendocytic sorting of seven-transmembrane-spanning G protein-coupled receptors
Abstract
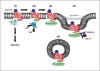
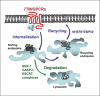
The largest superfamily of membrane proteins that translate extracellular signals into intracellular messages are the 7-transmembrane-spanning (7TM) G protein-coupled receptors (GPCR). One of the ways in which their activity is controlled is by the process of desensitization and endocytosis, whereby agonist-activated receptors are rapidly and often reversibly silenced through removal from the cell surface. Indeed, following endocytosis, individual receptors can be sorted differentially between recycling endosomes and lysosomes, which controls the reversibility of the silencing. Thus, endocytosis can either serve as a mechanism for receptor resensitization by delivering receptors back to the plasma membrane or facilitate receptor downregulation by serving as the first step towards targeting the receptors to lysosomes for degradation. The sorting of receptors to the lysosomal pathway can be facilitated by interaction with an array of accessory proteins. One of these proteins is the GPCR-associated sorting protein 1 (GASP-1), which specifically targets several 7TM-GPCR to the lysosomal pathway after endocytosis. Furthermore, GASP-1 was recently found to directly affect the signaling capacity of a 7TM-GPCR. Importantly, the in vivo relevance of GASP-1-dependent receptor sorting has also begun to be verified in animal models. Here, we summarize the recent advances in elucidating GASP-1-dependent receptor sorting functions and their potential implications in vivo.
Copyright 2010 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Modulation of postendocytic sorting of G protein-coupled receptors.Science. 2002 Jul 26;297(5581):615-20. doi: 10.1126/science.1073308. Science. 2002. PMID: 12142540
-
Postendocytic Sorting of Adrenergic and Opioid Receptors: New Mechanisms and Functions.Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2015;132:189-206. doi: 10.1016/bs.pmbts.2015.03.005. Epub 2015 Apr 11. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2015. PMID: 26055059 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dysbindin promotes the post-endocytic sorting of G protein-coupled receptors to lysosomes.PLoS One. 2010 Feb 19;5(2):e9325. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009325. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20174469 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in G protein-coupled receptor sorting protein affinity regulate postendocytic targeting of G protein-coupled receptors.J Biol Chem. 2007 Oct 5;282(40):29178-85. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M704014200. Epub 2007 Jul 16. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17635908
-
G protein-coupled receptor-associated sorting proteins: function and relevant disorders.Yi Chuan. 2020 Aug 20;42(8):713-724. doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.20-020. Yi Chuan. 2020. PMID: 32952108 Review.
Cited by
-
ARF6 and GASP-1 are post-endocytic sorting proteins selectively involved in the intracellular trafficking of dopamine D₂ receptors mediated by GRK and PKC in transfected cells.Br J Pharmacol. 2013 Mar;168(6):1355-74. doi: 10.1111/bph.12025. Br J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23082996 Free PMC article.
-
Functional screen identifies regulators of murine hematopoietic stem cell repopulation.J Exp Med. 2016 Mar 7;213(3):433-49. doi: 10.1084/jem.20150806. Epub 2016 Feb 15. J Exp Med. 2016. PMID: 26880577 Free PMC article.
-
Beclin 2 functions in autophagy, degradation of G protein-coupled receptors, and metabolism.Cell. 2013 Aug 29;154(5):1085-1099. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.07.035. Epub 2013 Aug 15. Cell. 2013. PMID: 23954414 Free PMC article.
-
The GPCR-associated sorting protein 1 regulates ligand-induced down-regulation of GPR55.Br J Pharmacol. 2012 Apr;165(8):2611-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01562.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 21718301 Free PMC article.
-
Pitchfork and Gprasp2 Target Smoothened to the Primary Cilium for Hedgehog Pathway Activation.PLoS One. 2016 Feb 22;11(2):e0149477. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0149477. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26901434 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Klabunde T, Hessler G. Drug design strategies for targeting G protein-coupled receptors. Chembiochem. 2002;3:928–944. - PubMed
-
- Gether U. Uncovering molecular mechanisms involved in activation of G protein-coupled receptors. Endocr Rev. 2000;21:90–113. - PubMed
-
- Claing A, Laporte SA, Caron MG, Lefkowitz RJ. Endocytosis of G protein-coupled receptors: roles of G protein-coupled receptor kinases and beta-arrestin proteins. Prog Neurobiol. 2002;66:61–79. - PubMed
-
- Wolfe BL, Trejo J. Clathrin-dependent mechanisms of G protein-coupled receptor endocytosis. Traffic. 2007;8:462–470. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

