Regulation of DNA-damage responses and cell-cycle progression by the chromatin remodelling factor CHD4
- PMID: 20693977
- PMCID: PMC2944064
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2010.188
Regulation of DNA-damage responses and cell-cycle progression by the chromatin remodelling factor CHD4
Abstract
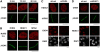
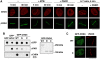
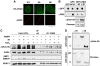
The chromatin remodelling factor chromodomain helicase DNA-binding protein 4 (CHD4) is a catalytic subunit of the NuRD transcriptional repressor complex. Here, we reveal novel functions for CHD4 in the DNA-damage response (DDR) and cell-cycle control. We show that CHD4 mediates rapid poly(ADP-ribose)-dependent recruitment of the NuRD complex to DNA-damage sites, and we identify CHD4 as a phosphorylation target for the apical DDR kinase ataxia-telangiectasia mutated. Functionally, we show that CHD4 promotes repair of DNA double-strand breaks and cell survival after DNA damage. In addition, we show that CHD4 acts as an important regulator of the G1/S cell-cycle transition by controlling p53 deacetylation. These results provide new insights into how the chromatin remodelling complex NuRD contributes to maintaining genome stability.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
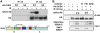
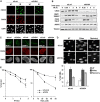
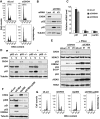
References
-
- Ahel I, Ahel D, Matsusaka T, Clark AJ, Pines J, Boulton SJ, West SC (2008) Poly(ADP-ribose)-binding zinc finger motifs in DNA repair/checkpoint proteins. Nature 451: 81–85 - PubMed
-
- Bao Y, Shen X (2007) Chromatin remodeling in DNA double-strand break repair. Curr Opin Genet Dev 17: 126–131 - PubMed
-
- Caldecott KW (2008) Single-strand break repair and genetic disease. Nat Rev Genet 9: 619–631 - PubMed
-
- Carter S, Vousden KH (2009) Modifications of p53: competing for the lysines. Curr Opin Genet Dev 19: 18–24 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

