MICU1 encodes a mitochondrial EF hand protein required for Ca(2+) uptake
- PMID: 20693986
- PMCID: PMC2977980
- DOI: 10.1038/nature09358
MICU1 encodes a mitochondrial EF hand protein required for Ca(2+) uptake
Abstract
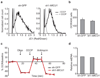
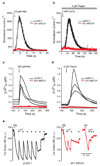
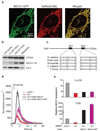
Mitochondrial calcium uptake has a central role in cell physiology by stimulating ATP production, shaping cytosolic calcium transients and regulating cell death. The biophysical properties of mitochondrial calcium uptake have been studied in detail, but the underlying proteins remain elusive. Here we use an integrative strategy to predict human genes involved in mitochondrial calcium entry based on clues from comparative physiology, evolutionary genomics and organelle proteomics. RNA interference against 13 top candidates highlighted one gene, CBARA1, that we call hereafter mitochondrial calcium uptake 1 (MICU1). Silencing MICU1 does not disrupt mitochondrial respiration or membrane potential but abolishes mitochondrial calcium entry in intact and permeabilized cells, and attenuates the metabolic coupling between cytosolic calcium transients and activation of matrix dehydrogenases. MICU1 is associated with the mitochondrial inner membrane and has two canonical EF hands that are essential for its activity, indicating a role in calcium sensing. MICU1 represents the founding member of a set of proteins required for high-capacity mitochondrial calcium uptake. Its discovery may lead to the complete molecular characterization of mitochondrial calcium uptake pathways, and offers genetic strategies for understanding their contribution to normal physiology and disease.
Figures
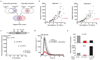
Comment in
-
Cell biology: A sensor for calcium uptake.Nature. 2010 Sep 16;467(7313):283. doi: 10.1038/467283a. Nature. 2010. PMID: 20844529 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vasington FD, Murphy JV. Ca ion uptake by rat kidney mitochondria and its dependence on respiration and phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1962;237:2670–2677. - PubMed
-
- Rizzuto R, Simpson AW, Brini M, Pozzan T. Rapid changes of mitochondrial Ca2+ revealed by specifically targeted recombinant aequorin. Nature. 1992;358:325–327. - PubMed
-
- Filippin L, Magalhaes PJ, Di Benedetto G, Colella M, Pozzan T. Stable interactions between mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum allow rapid accumulation of calcium in a subpopulation of mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:39224–39234. - PubMed
-
- Palmer AE, et al. Ca2+ indicators based on computationally redesigned calmodulin-peptide pairs. Chem Biol. 2006;13:521–530. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

