Mycobacterium tuberculosis lipoprotein LprG (Rv1411c) binds triacylated glycolipid agonists of Toll-like receptor 2
- PMID: 20694006
- PMCID: PMC2933325
- DOI: 10.1038/nsmb.1869
Mycobacterium tuberculosis lipoprotein LprG (Rv1411c) binds triacylated glycolipid agonists of Toll-like receptor 2
Abstract
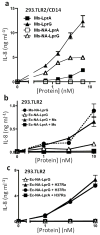
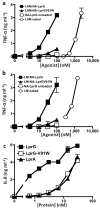
Knockout of lprG results in decreased virulence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) in mice. MTB lipoprotein LprG has TLR2 agonist activity, which is thought to be dependent on its N-terminal triacylation. Unexpectedly, here we find that nonacylated LprG retains TLR2 activity. Moreover, we show LprG association with triacylated glycolipid TLR2 agonists lipoarabinomannan, lipomannan and phosphatidylinositol mannosides (which share core structures). Binding of triacylated species was specific to LprG (not LprA) and increased LprG TLR2 agonist activity; conversely, association of glycolipids with LprG enhanced their recognition by TLR2. The crystal structure of LprG in complex with phosphatidylinositol mannoside revealed a hydrophobic pocket that accommodates the three alkyl chains of the ligand. In conclusion, we demonstrate a glycolipid binding function of LprG that enhances recognition of triacylated MTB glycolipids by TLR2 and may affect glycolipid assembly or transport for bacterial cell wall biogenesis.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Mycobacterium tuberculosis Lipoprotein and Lipoglycan Binding to Toll-Like Receptor 2 Correlates with Agonist Activity and Functional Outcomes.Infect Immun. 2018 Sep 21;86(10):e00450-18. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00450-18. Print 2018 Oct. Infect Immun. 2018. PMID: 30037791 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structure and functional implications of LprF from Mycobacterium tuberculosis and M. bovis.Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2014 Oct;70(Pt 10):2619-30. doi: 10.1107/S1399004714016599. Epub 2014 Sep 27. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2014. PMID: 25286846
-
Mycobacterium tuberculosis lipoprotein LprG binds lipoarabinomannan and determines its cell envelope localization to control phagolysosomal fusion.PLoS Pathog. 2014 Oct 30;10(10):e1004471. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004471. eCollection 2014 Oct. PLoS Pathog. 2014. PMID: 25356793 Free PMC article.
-
Lipoarabinomannan, and its related glycolipids, induce divergent and opposing immune responses to Mycobacterium tuberculosis depending on structural diversity and experimental variations.Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2016 Jan;96:120-30. doi: 10.1016/j.tube.2015.09.005. Epub 2015 Oct 28. Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2016. PMID: 26586646 Review.
-
Immunological hyporesponsiveness in tuberculosis: The role of mycobacterial glycolipids.Front Immunol. 2022 Dec 2;13:1035122. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1035122. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36544778 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Poly-γ-d-Glutamic Acid Capsule Surrogate of the Bacillus anthracis Capsule Is a Novel Toll-Like Receptor 2 Agonist.Infect Immun. 2015 Oct;83(10):3847-56. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00888-15. Epub 2015 Jul 20. Infect Immun. 2015. PMID: 26195551 Free PMC article.
-
Critical discussion on drug efflux in Mycobacterium tuberculosis.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2022 Feb 9;46(1):fuab050. doi: 10.1093/femsre/fuab050. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2022. PMID: 34637511 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of P27 -P55 operon from Mycobacterium tuberculosis in the resistance to toxic compounds.BMC Infect Dis. 2011 Jul 16;11:195. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-11-195. BMC Infect Dis. 2011. PMID: 21762531 Free PMC article.
-
The role of transport mechanisms in mycobacterium tuberculosis drug resistance and tolerance.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2012 Nov 9;5(11):1210-35. doi: 10.3390/ph5111210. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2012. PMID: 24281307 Free PMC article.
-
LprG-mediated surface expression of lipoarabinomannan is essential for virulence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis.PLoS Pathog. 2014 Sep 18;10(9):e1004376. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004376. eCollection 2014 Sep. PLoS Pathog. 2014. PMID: 25232742 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
- AI027243/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI007061/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI071155/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HL055967/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AI069085/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI035726/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI068135/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI071155/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI067093/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI035726/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL055967/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AI049313/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI034343/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI034343/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI027243/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI069085/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI068135/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI049313/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI067093/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

