Complement regulator CD46 temporally regulates cytokine production by conventional and unconventional T cells
- PMID: 20694009
- PMCID: PMC4011020
- DOI: 10.1038/ni.1917
Complement regulator CD46 temporally regulates cytokine production by conventional and unconventional T cells
Abstract
In this study we demonstrate a new form of immunoregulation: engagement on CD4(+) T cells of the complement regulator CD46 promoted the effector potential of T helper type 1 cells (T(H)1 cells), but as interleukin 2 (IL-2) accumulated, it switched cells toward a regulatory phenotype, attenuating IL-2 production via the transcriptional regulator ICER/CREM and upregulating IL-10 after interaction of the CD46 tail with the serine-threonine kinase SPAK. Activated CD4(+) T cells produced CD46 ligands, and blocking CD46 inhibited IL-10 production. Furthermore, CD4(+) T cells in rheumatoid arthritis failed to switch, consequently producing excessive interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma). Finally, gammadelta T cells, which rarely produce IL-10, expressed an alternative CD46 isoform and were unable to switch. Nonetheless, coengagement of T cell antigen receptor (TCR) gammadelta and CD46 suppressed effector cytokine production, establishing that CD46 uses distinct mechanisms to regulate different T cell subsets during an immune response.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

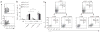
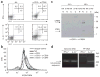

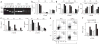
References
-
- Moore KW, de Waal Malefyt R, Coffman RL, O’Garra A. Interleukin-10 and the interleukin-10 receptor. Annu Rev Immunol. 2001;19:683–765. - PubMed
-
- Gazzinelli RT, et al. In the absence of endogenous IL-10, mice acutely infected with Toxoplasma gondii succumb to a lethal immune response dependent on CD4+ T cells and accompanied by overproduction of IL-12, IFN-γ and TNF-α. J Immunol. 1996;157:798–805. - PubMed
-
- O’Garra A, Vieira P. TH1 cells control themselves by producing interleukin-10. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007;7:425–428. - PubMed
-
- Kuhn R, Lohler J, Rennick D, Rajewsky K, Muller W. Interleukin-10-deficient mice develop chronic enterocolitis. Cell. 1993;75:263–274. - PubMed
-
- Franke A, et al. Sequence variants in IL10, ARPC2 and multiple other loci contribute to ulcerative colitis susceptibility. Nat Genet. 2008;40:1319–1323. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

