Inhibitory actions of mibefradil on steroidogenesis in mouse Leydig cells: involvement of Ca(2+) entry via the T-type Ca(2+) channel
- PMID: 20694017
- PMCID: PMC3739071
- DOI: 10.1038/aja.2010.51
Inhibitory actions of mibefradil on steroidogenesis in mouse Leydig cells: involvement of Ca(2+) entry via the T-type Ca(2+) channel
Abstract
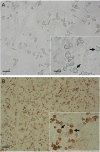
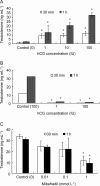
Intracellular cAMP and Ca(2+) are involved in the regulation of steroidogenic activity in Leydig cells, which coordinate responses to luteinizing hormone (LH) and human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). However, the identification of Ca(2+) entry implicated in Leydig cell steroidogenesis is not well defined. The objective of this study was to identify the type of Ca(2+) channel that affects Leydig cell steroidogenesis. In vitro steroidogenesis in the freshly dissociated Leydig cells of mice was induced by hCG incubation. The effects of mibefradil (a putative T-type Ca(2+) channel blocker) on steroidogenesis were assessed using reverse transcription (RT)-polymerase chain reaction analysis for the steroidogenic acute regulatory protein (StAR) mRNA expression and testosterone production using radioimmunoassay. In the presence of 1.0 mmol L(-1) extracellular Ca(2+), hCG at 1 to 100 IU noticeably elevated both StAR mRNA level and testosterone secretion (P < 0.05), and the stimulatory effects of hCG were markedly diminished by mibefradil in a dose-dependent manner (P < 0.05). Moreover, the hCG-induced increase in testosterone production was completely removed when external Ca(2+) was omitted, implying that Ca(2+) entry is needed for hCG-induced steroidogenesis. Furthermore, a patch-clamp study revealed the presence of mibefradil-sensitive Ca(2+) currents seen at a concentration range that nearly paralleled those inhibiting steroidogenesis. Collectively, our data provide evidence that hCG-stimulated steroidogenesis is mediated at least in part by Ca(2+) entry carried out by the T-type Ca(2+) channel in the Leydig cells of mice.
Figures


References
-
- Dufau ML. Endocrine regulation and communicating functions of the Leydig cell. Ann Rev Physiol. 1988;50:483–508. - PubMed
-
- Saez JM. Leydig cells: endocrine, paracrine, and autocrine regulation. Endocr Rev. 1994;15:574–626. - PubMed
-
- Chen YC, Nagpal ML, Stocco DM, Lin T. Effects of genistein, resveratrol, and quercetin on steroidogenesis and proliferation of MA-10 mouse Leydig tumor cells. J Endocrinol. 2007;192:527–37. - PubMed
-
- Medelson C, Dufau ML, Catt KJ. Gonadotropin binding and stimulation of cAMP and testosterone production in isolated Leydig cells. J Biol Chem. 1975;250:8818–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

