Lipo-oligoarginines as effective delivery vectors to promote cellular uptake
- PMID: 20694264
- PMCID: PMC3156442
- DOI: 10.1039/c004684a
Lipo-oligoarginines as effective delivery vectors to promote cellular uptake
Abstract
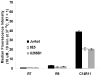
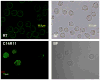
An effective cellular delivery vector with enhanced intracellular retention was developed by conjugating a cell-penetrating peptide (CPP) with a fatty acid chain. The optimized lipopeptide (LP), myristoylated hendecaarginine (C14R11), penetrated the cell membrane with high efficiency, and achieved superior metabolic stability and versatility as compared with unmodified oligoarginine CPPs, offering no adverse effect on cell viability and function. Cellular uptake, intracellular localization, cytotoxicity, and release kinetics of oligoarginines and LPs were investigated using flow cytometry analysis, cytotoxicity assay, and confocal microscopy. The cellular uptake efficiency and intracellular metabolic stability of C14R11 LP was further enhanced by replacing the L-arginine residues with D-arginine isomers. The cellular uptake and intracellular metabolic stability of D-form C14R11 (C14dR11) was significantly increased without any noticeable cytotoxicity compared to the unmodified parent hepta-arginine CPP or L-arginine LPs.
Figures





References
-
- Frankel AD, Pabo CO. Cell. 1988;55:1189–1193. - PubMed
-
- Green M, Loewenstein PM. Cell. 1988;55:1179–1188. - PubMed
-
- Joliot AH, Triller A, Volovitch M, Pernelle C, Prochiantz A. New Biol. 1991;3:1121–1134. - PubMed
-
- Derossi D, Calvet S, Trembleau A, Brunissen A, Chassaing G, Prochiantz A. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:18188–18193. - PubMed
-
- Vives E, Brodin P, Lebleu B. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:16010–16017. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

