Formulation of dacarbazine-loaded cubosomes. Part III. Physicochemical characterization
- PMID: 20694534
- PMCID: PMC2974159
- DOI: 10.1208/s12249-010-9496-7
Formulation of dacarbazine-loaded cubosomes. Part III. Physicochemical characterization
Abstract
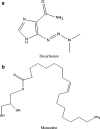
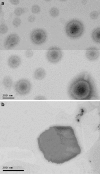
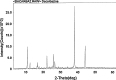
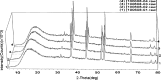
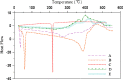
The purpose of this study was to investigate the physicochemical properties of dacarbazine-loaded cubosomes. The drug-loaded cubosome nanocarriers were prepared by a fragmentation method and then freeze dried. They were then characterized for size, morphology, thermal behavior, and crystallography using dynamic light scattering, transmission electron microscopy (TEM), differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), and powder X-ray diffraction (PXRD), respectively. The drug loading and encapsulation efficiency were determined by UV spectrophotometry. The results showed that the prepared dacarbazine-loaded cubosomes had mean diameters ranging from 86 to 106 nm. In addition to the TEM, the characteristic peaks from PXRD data suggested that the freeze-dried nanoformulations were indeed cubic in nature. DSC and PXRD analysis suggested the 0.06 or 0.28% w/w actual drug loaded inside cubosomes was in the amorphous or molecular state. These physicochemical characteristics would affect the nanoformulation shelf-life, efficacy, and safety.
Figures
References
-
- Chiappetta DA, Carcaboso AM, Bregni C, Rubio M, Bramuglia G, Sosnik A. Indinavir-loaded pH-sensitive microparticles for taste masking: toward extemporaneous pediatric anti-HIV/AIDS liquid formulations with improved patient compliance. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2009;10(1):1–6. doi: 10.1208/s12249-008-9168-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

