A Phase 1 study of UCN-01 in combination with irinotecan in patients with resistant solid tumor malignancies
- PMID: 20694727
- PMCID: PMC3102212
- DOI: 10.1007/s00280-010-1410-1
A Phase 1 study of UCN-01 in combination with irinotecan in patients with resistant solid tumor malignancies
Abstract
Purpose: UCN-01 (7-hydroxystaurosporine) is a multi-targeted protein kinase inhibitor that exhibits synergistic activity with DNA-damaging agents in preclinical studies. We conducted a Phase I study to determine the maximum-tolerated dose (MTD), dose-limiting toxicity (DLT), pharmacokinetic, and pharmacodynamic effects of UCN-01 and irinotecan in patients with resistant solid tumors.
Experimental design: Patients received irinotecan (75-125 mg/m(2) IV on days 1, 8, 15, 22) and UCN-01 (50-90 mg/m(2) IV on day 2 and 25-45 mg/m(2) on day 23 and subsequent doses) every 42 days. Blood for pharmacokinetics of UCN-01 and irinotecan, and blood, normal rectal mucosa, and tumor biopsies for pharmacodynamic studies were obtained.
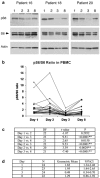
Results: Twenty-five patients enrolled to 5 dose levels. The MTD was irinotecan 125 mg/m(2) on days 1, 8, 15, 22 and UCN-01 70 mg/m(2) on day 2 and 35 mg/m(2) on day 23. DLTs included grade 3 diarrhea/dehydration and dyspnea. UCN-01 had a prolonged half-life and a low clearance rate. There was a significant reduction in SN-38 C(max) and aminopentanocarboxylic acid (APC) and SN-38 glucuronide half-lives. Phosphorylated ribosomal protein S6 was reduced in blood, normal rectal mucosa, and tumor biopsies at 24 h post-UCN-01. Two partial responses were observed in women with ER, PgR, and HER2-negative breast cancers (TBNC). Both tumors were defective for p53. Twelve patients had stable disease (mean duration 18 weeks, range 7-30 weeks).
Conclusion: UCN-01 and irinotecan demonstrated acceptable toxicity and target inhibition. Anti-tumor activity was observed and a study of this combination in women with TNBC is underway.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Phase I and pharmacokinetic study of UCN-01 in combination with irinotecan in patients with solid tumors.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2008 Mar;61(3):423-33. doi: 10.1007/s00280-007-0485-9. Epub 2007 Apr 12. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 17429623 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A phase II study of UCN-01 in combination with irinotecan in patients with metastatic triple negative breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2013 Jan;137(2):483-92. doi: 10.1007/s10549-012-2378-9. Epub 2012 Dec 15. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2013. PMID: 23242585 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A phase I trial of UCN-01 and prednisone in patients with refractory solid tumors and lymphomas.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2010 Jan;65(2):383-9. doi: 10.1007/s00280-009-1154-y. Epub 2009 Nov 6. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 19894051 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Phase I dose escalation trial of weekly docetaxel plus irinotecan in patients with advanced cancer.Cancer Biol Ther. 2002 Nov-Dec;1(6):646-51. doi: 10.4161/cbt.314. Cancer Biol Ther. 2002. PMID: 12642688 Review.
-
Phase I study of weekly CPT-11 (irinotecan)/docetaxel in patients with advanced solid tumors.Lung Cancer. 2002 Aug;37(2):213-8. doi: 10.1016/s0169-5002(02)00081-8. Lung Cancer. 2002. PMID: 12140145 Review.
Cited by
-
UCN-01 induces S and G2/M cell cycle arrest through the p53/p21(waf1) or CHK2/CDC25C pathways and can suppress invasion in human hepatoma cell lines.BMC Cancer. 2013 Mar 28;13:167. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-13-167. BMC Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23537372 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-species genomic and functional analyses identify a combination therapy using a CHK1 inhibitor and a ribonucleotide reductase inhibitor to treat triple-negative breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res. 2012 Jul 19;14(4):R109. doi: 10.1186/bcr3230. Breast Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22812567 Free PMC article.
-
A phase II study of cell cycle inhibitor UCN-01 in patients with metastatic melanoma: a California Cancer Consortium trial.Invest New Drugs. 2012 Apr;30(2):741-8. doi: 10.1007/s10637-010-9562-8. Epub 2010 Oct 22. Invest New Drugs. 2012. PMID: 20967484 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
DNA damage response in breast cancer and its significant role in guiding novel precise therapies.Biomark Res. 2024 Sep 27;12(1):111. doi: 10.1186/s40364-024-00653-2. Biomark Res. 2024. PMID: 39334297 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthetic lethality of Chk1 inhibition combined with p53 and/or p21 loss during a DNA damage response in normal and tumor cells.Oncogene. 2013 Jan 31;32(5):577-88. doi: 10.1038/onc.2012.84. Epub 2012 Mar 19. Oncogene. 2013. PMID: 22430210 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abramoff MD. Roaming through methodology XXIX. P. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2001;145:602. - PubMed
-
- Akiyama T, Shimizu M, Okabe M, Tamaoki T, Akinaga S. Differential effects of UCN-01, staurosporine and CGP 41 251 on cell cycle progression and CDC2/cyclin B1 regulation in A431 cells synchronized at M phase by nocodazole. Anticancer Drugs. 1999;10:67–78. doi: 10.1097/00001813-199901000-00009. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

