Triosephosphate isomerase: a highly evolved biocatalyst
- PMID: 20694739
- PMCID: PMC11115733
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-010-0473-9
Triosephosphate isomerase: a highly evolved biocatalyst
Abstract
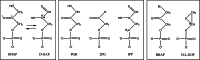
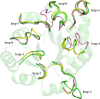
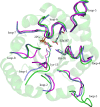
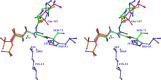
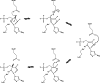
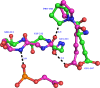
Triosephosphate isomerase (TIM) is a perfectly evolved enzyme which very fast interconverts dihydroxyacetone phosphate and D: -glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate. Its catalytic site is at the dimer interface, but the four catalytic residues, Asn11, Lys13, His95 and Glu167, are from the same subunit. Glu167 is the catalytic base. An important feature of the TIM active site is the concerted closure of loop-6 and loop-7 on ligand binding, shielding the catalytic site from bulk solvent. The buried active site stabilises the enediolate intermediate. The catalytic residue Glu167 is at the beginning of loop-6. On closure of loop-6, the Glu167 carboxylate moiety moves approximately 2 Å to the substrate. The dynamic properties of the Glu167 side chain in the enzyme substrate complex are a key feature of the proton shuttling mechanism. Two proton shuttling mechanisms, the classical and the criss-cross mechanism, are responsible for the interconversion of the substrates of this enolising enzyme.
Figures









References
-
- Knowles JR, Albery WJ. Perfection in enzyme catalysis: the energetics of triosephosphate isomerase. Acc Chem Res. 1977;10:105–111. doi: 10.1021/ar50112a001. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

