Penetration of linezolid into rabbit intervertebral discs and surrounding tissues
- PMID: 20694846
- PMCID: PMC2997209
- DOI: 10.1007/s00586-010-1548-x
Penetration of linezolid into rabbit intervertebral discs and surrounding tissues
Abstract
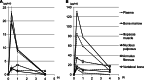
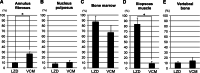
Linezolid belongs to a new class of synthetic antimicrobial agent that is effective for a variety of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infections including bone and joint MRSA infections, but the effectiveness of linezolid for the treatment of MRSA spine infection remains controversial. In this study, we investigated the diffusion of linezolid or vancomycin into normal rabbit spinal tissues to determine the adequacy of linezolid for the treatment of spinal infection. The penetration efficacy of linezolid into the annulus fibrosus, nucleus pulposus, and vertebral bone (10, 8, and 10%, respectively) was lower than that of vancomycin (27, 11, and 14%, respectively). The penetration efficacy of linezolid into the bone marrow and iliopsoas muscle (88 and 84%, respectively), however, was higher than that of vancomycin (67 and 9%, respectively). These results suggest that linezolid is inadequate for the treatment of spine infection limited to the intervertebral disc, but may be effective for the treatment of infection extending into the muscle and bone marrow, such as in vertebral osteomyelitis, iliopsoas abscess, and postsurgical infection.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

