Discounting of delayed rewards and executive dysfunction in individuals infected with hepatitis C
- PMID: 20694872
- PMCID: PMC3615977
- DOI: 10.1080/13803395.2010.499355
Discounting of delayed rewards and executive dysfunction in individuals infected with hepatitis C
Abstract
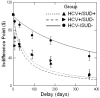
Objective: Determine whether adults with hepatitis C (HCV), regardless of substance use disorder, are more likely to discount delayed rewards than adults without hepatitis C, and explore the relationship between delay discounting and neuropsychological functioning.
Methods: Procedures included clinical interviews, neuropsychological testing, and a delay discounting task.
Results: Regardless of substance abuse history, adults with hepatitis C were significantly more likely to choose smaller immediate rewards over larger delayed rewards. Delay discounting correlated with performance on executive functioning tasks.
Conclusions: Increased discounting is associated with broad executive dysfunction, suggesting that HCV-associated executive dysfunction may lead to altered decision-making style.
Figures

References
-
- Ainslie G. Specious reward: a behavioral theory of impulsiveness and impulse control. Psychological Bulletin. 1975;82:463–496. - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Association . Diagnostic and statistical manual for mental disorders. American Psychiatric Association; Washington, DC: 2000. Fourth Edition, Text Revision ed.
-
- Aron JL, Paulus MP. Location, location: Using functional magnetic resonance imaging to pinpoint brain differences relevant to stimulant use. Addiction. 2007;102:33–43. - PubMed
-
- Baker F, Johnson MW, Bickel WK. Delay discouting in current and never-before cigarette smokers: similarities and differences among commodity, sign, and magnitude. Journal of Abnormal Psychology. 2003;112:382–392. - PubMed
-
- Beck A.t., Steer RA, Brown GK. Beck Depression Inventory Manual, Second Edition. Psychological Corporation; New York: 1996.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
