Conditioning with masked stimuli affects the timecourse of skin conductance responses
- PMID: 20695647
- PMCID: PMC5275764
- DOI: 10.1037/a0019927
Conditioning with masked stimuli affects the timecourse of skin conductance responses
Abstract
In Pavlovian fear conditioning, an aversive unconditional stimulus (UCS) is repeatedly paired with a neutral conditional stimulus (CS). As a consequence, the subject begins to show conditional responses (CRs) to the CS that indicate expectation and fear. There are currently two general models competing to explain the role of subjective awareness in fear conditioning. Proponents of the single-process model assert that a single propositional learning process mediates CR expression and UCS expectancy. Proponents of a dual-process model assert that these behavioral responses are expressions of two independent learning processes. We used backward masking to block perception of our visual CSs and measured the effect of this training on subsequent unmasked performance. In two separate experiments we show a dissociation between CR expression and UCS expectancy following differential delay conditioning with masked CSs. In Experiment I, we show that masked training facilitates CR expression when the same CSs are presented during a subsequent unmasked reacquisition task. In Experiment II we show that masked training retards learning when the CS+ is presented as part of a compound CS during a subsequent unmasked blocking task. Our results suggest that multiple memory systems operate in a parallel, independent manner to encode emotional memories.
2010 APA, all rights reserved.
Figures


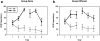




References
-
- Bechara A, Tranel D, Damasio H, Adolphs R, Rockland C, Damasio AR. Double dissociation of conditioning and declarative knowledge relative to the amygdala and hippocampus in humans. Science. 1995;269:1115–1118. doi:10.1126/science.7652558. - PubMed
-
- Carter RM, O'Doherty JP, Seymour B, Koch C, Dolan RJ. Contingency awareness in human aversive conditioning involves the middle frontal gyrus. Neuroimage. 2006;29:1007–1012. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2005.09.011. - PubMed
-
- Cheng DT, Knight DC, Smith CN, Stein EA, Helmstetter FJ. Functional MRI of human amygdala activity during Pavlovian fear conditioning: Stimulus processing versus response expression. Behavioral Neuroscience. 2003;117:3–10. doi:10.1037/0735–7044.117.1.3. - PubMed
-
- Clark RE, Manns JR, Squire LR. Classical conditioning, awareness, and brain systems. Trends in Cognitive Sciences. 2002;6:524–531. doi:10.1016/S1364-6613(02)02041–7. - PubMed
-
- Clark RE, Squire LR. Classical conditioning and brain systems: The role of awareness. Science. 1998;280:77–81. doi:10.1126/science.280.5360.77. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

