Agrobacterium-produced and exogenous cytokinin-modulated Agrobacterium-mediated plant transformation
- PMID: 20696005
- PMCID: PMC6640272
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1364-3703.2010.00637.x
Agrobacterium-produced and exogenous cytokinin-modulated Agrobacterium-mediated plant transformation
Abstract
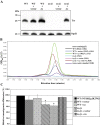
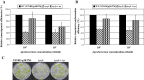
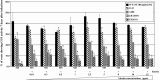
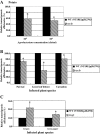
Agrobacterium tumefaciens is a plant pathogenic bacterium that causes neoplastic growths, called 'crown gall', via the transfer and integration of transferred DNA (T-DNA) from the bacterium into the plant genome. We characterized an acetosyringone (AS)-induced tumour-inducing (Ti) plasmid gene, tzs (trans-zeatin synthesizing), that is responsible for the synthesis of the plant hormone cytokinin in nopaline-type A. tumefaciens strains. The loss of Tzs protein expression and trans-zeatin secretions by the tzs frameshift (tzs-fs) mutant is associated with reduced tumorigenesis efficiency on white radish stems and reduced transformation efficiencies on Arabidopsis roots. Complementation of the tzs-fs mutant with a wild-type tzs gene restored wild-type levels of trans-zeatin secretions and transformation efficiencies. Exogenous application of cytokinin during infection increased the transient transformation efficiency of Arabidopsis roots infected by strains lacking Tzs, which suggests that the lower transformation efficiency resulted from the lack of Agrobacterium-produced cytokinin. Interestingly, although the tzs-fs mutant displayed reduced tumorigenesis efficiency on several tested plants, the loss of Tzs enhanced tumorigenesis efficiencies on green pepper and cowpea. These data strongly suggest that Tzs, by synthesizing trans-zeatin at early stage(s) of the infection process, modulates plant transformation efficiency by A. tumefaciens.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Tzs protein and exogenous cytokinin affect virulence gene expression and bacterial growth of Agrobacterium tumefaciens.Phytopathology. 2013 Sep;103(9):888-99. doi: 10.1094/PHYTO-01-13-0020-R. Phytopathology. 2013. PMID: 23593941
-
Biological activity of the tzs gene of nopaline Agrobacterium tumefaciens GV3101 in plant regeneration and genetic transformation.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2013 Nov;26(11):1359-65. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-04-13-0106-R. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2013. PMID: 24088018
-
Constitutive expression of the tzs gene from Agrobacterium tumefaciens virG mutant strains is responsible for improved transgenic plant regeneration in cotton meristem transformation.Plant Cell Rep. 2016 Mar;35(3):601-11. doi: 10.1007/s00299-015-1906-6. Epub 2015 Dec 9. Plant Cell Rep. 2016. PMID: 26650837
-
Transcriptome Profiling of Plant Genes in Response to Agrobacterium tumefaciens-Mediated Transformation.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2018;418:319-348. doi: 10.1007/82_2018_115. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30062593 Review.
-
The Ti Plasmid, Driver of Agrobacterium Pathogenesis.Phytopathology. 2023 Apr;113(4):594-604. doi: 10.1094/PHYTO-11-22-0432-IA. Epub 2023 Apr 26. Phytopathology. 2023. PMID: 37098885 Review.
Cited by
-
Ecological Conditions and Molecular Determinants Involved in Agrobacterium Lifestyle in Tumors.Front Plant Sci. 2019 Jul 30;10:978. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.00978. eCollection 2019. Front Plant Sci. 2019. PMID: 31417593 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cytokinins mediate resistance against Pseudomonas syringae in tobacco through increased antimicrobial phytoalexin synthesis independent of salicylic acid signaling.Plant Physiol. 2011 Oct;157(2):815-30. doi: 10.1104/pp.111.182931. Epub 2011 Aug 3. Plant Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21813654 Free PMC article.
-
Sound Vibration-Triggered Epigenetic Modulation Induces Plant Root Immunity Against Ralstonia solanacearum.Front Microbiol. 2020 Aug 21;11:1978. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.01978. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32973716 Free PMC article.
-
Agrobacterium: nature's genetic engineer.Front Plant Sci. 2015 Jan 6;5:730. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2014.00730. eCollection 2014. Front Plant Sci. 2015. PMID: 25610442 Free PMC article.
-
Cytokinin Regulation of Source-Sink Relationships in Plant-Pathogen Interactions.Front Plant Sci. 2021 Aug 24;12:677585. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.677585. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 34504504 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

