Identification of a novel homozygous nonsense mutation in EYS in a Chinese family with autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa
- PMID: 20696082
- PMCID: PMC2927534
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2350-11-121
Identification of a novel homozygous nonsense mutation in EYS in a Chinese family with autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa
Abstract
Background: Retinitis pigmentosa is the most important hereditary retinal degenerative disease, which has a high degree of clinical and genetic heterogeneity. More than half of all cases of retinitis pigmentosa are autosomal recessive (arRP), but the gene(s) causing arRP in most families has yet to be identified. The purpose of this study is to identify the genetic basis of severe arRP in a consanguineous Chinese family.
Methods: Linkage and haplotype analyses were used to define the chromosomal location of the pathogenic gene in the Chinese arRP family. Direct DNA sequence analysis of the entire coding region and exon-intron boundaries of EYS was used to determine the disease-causing mutation, and to demonstrate that the mutation co-segregates with the disease in the family.
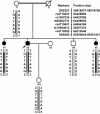
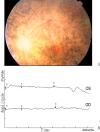
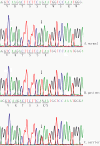
Results: A single nucleotide substitution of G to T at nucleotide 5506 of EYS was identified in the Chinese arRP family. This change caused a substitution of a glutamic acid residue at codon 1,836 by a stop codon TAA (p.E1836X), and resulted in a premature truncated EYS protein with 1,835 amino acids. Three affected siblings in the family were homozygous for the p.E1836X mutation, while the other unaffected family members carried one mutant allele and one normal EYS allele. The nonsense mutation p.E1836X was not detected in 200 unrelated normal controls.
Conclusions: The EYS gene is a recently identified disease-causing gene for retinitis pigmentosa, and encodes the orthologue of Drosophila spacemaker. To date, there are only eight mutations in EYS that have been identified to cause arRP. Here we report one novel homozygous nonsense mutation of EYS in a consanguineous Chinese arRP family. Our study represents the first independent confirmation that mutations in EYS cause arRP. Additionally, this is the first EYS mutation identified in the Chinese population.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Two novel mutations in the EYS gene are possible major causes of autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa in the Japanese population.PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e31036. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0031036. Epub 2012 Feb 17. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22363543 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a 2 Mb human ortholog of Drosophila eyes shut/spacemaker that is mutated in patients with retinitis pigmentosa.Am J Hum Genet. 2008 Nov;83(5):594-603. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2008.10.014. Epub 2008 Oct 30. Am J Hum Genet. 2008. PMID: 18976725 Free PMC article.
-
Missense mutations at homologous positions in the fourth and fifth laminin A G-like domains of eyes shut homolog cause autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa.Mol Vis. 2010 Dec 15;16:2753-9. Mol Vis. 2010. PMID: 21179430 Free PMC article.
-
Ocular genetics in the Japanese population.Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2024 Sep;68(5):401-418. doi: 10.1007/s10384-024-01109-8. Epub 2024 Sep 14. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 39271608 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Retinitis pigmentosa genes implicated in South Asian populations: a systematic review.J Pak Med Assoc. 2017 Nov;67(11):1734-1739. J Pak Med Assoc. 2017. PMID: 29171570
Cited by
-
Targeted next-generation sequencing extends the phenotypic and mutational spectrums for EYS mutations.Mol Vis. 2016 Jun 16;22:646-57. eCollection 2016. Mol Vis. 2016. PMID: 27375351 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-exome Sequencing Analysis Identifies Mutations in the EYS Gene in Retinitis Pigmentosa in the Indian Population.Sci Rep. 2016 Jan 20;6:19432. doi: 10.1038/srep19432. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26787102 Free PMC article.
-
Histopathological comparison of eyes from patients with autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa caused by novel EYS mutations.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2015 Feb;253(2):295-305. doi: 10.1007/s00417-014-2868-z. Epub 2014 Dec 11. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2015. PMID: 25491159 Free PMC article.
-
Ablation of EYS in zebrafish causes mislocalisation of outer segment proteins, F-actin disruption and cone-rod dystrophy.Sci Rep. 2017 Apr 5;7:46098. doi: 10.1038/srep46098. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28378834 Free PMC article.
-
Dissecting the role of EYS in retinal degeneration: clinical and molecular aspects and its implications for future therapy.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2021 May 17;16(1):222. doi: 10.1186/s13023-021-01843-z. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2021. PMID: 34001227 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tous HM, Izquierdo NJ. Retinitis pigmentosa in Puerto Rico. P R Health Sci J. 2006;25(4):315–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

