Tocotrienols, the vitamin E of the 21st century: its potential against cancer and other chronic diseases
- PMID: 20696139
- PMCID: PMC2956867
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bcp.2010.07.043
Tocotrienols, the vitamin E of the 21st century: its potential against cancer and other chronic diseases
Abstract
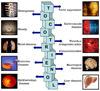
Initially discovered in 1938 as a "fertility factor," vitamin E now refers to eight different isoforms that belong to two categories, four saturated analogues (α, β, γ, and δ) called tocopherols and four unsaturated analogues referred to as tocotrienols. While the tocopherols have been investigated extensively, little is known about the tocotrienols. Very limited studies suggest that both the molecular and therapeutic targets of the tocotrienols are distinct from those of the tocopherols. For instance, suppression of inflammatory transcription factor NF-κB, which is closely linked to tumorigenesis and inhibition of HMG-CoA reductase, mammalian DNA polymerases and certain protein tyrosine kinases, is unique to the tocotrienols. This review examines in detail the molecular targets of the tocotrienols and their roles in cancer, bone resorption, diabetes, and cardiovascular and neurological diseases at both preclinical and clinical levels. As disappointment with the therapeutic value of the tocopherols grows, the potential of these novel vitamin E analogues awaits further investigation.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures





References
-
- Qureshi AA, Sami SA, Salser WA, Khan FA. Synergistic effect of tocotrienol-rich fraction (TRF(25)) of rice bran and lovastatin on lipid parameters in hypercholesterolemic humans. J Nutr Biochem. 2001;12:318–329. - PubMed
-
- Qureshi AA, Sami SA, Salser WA, Khan FA. Dose-dependent suppression of serum cholesterol by tocotrienol-rich fraction (TRF25) of rice bran in hypercholesterolemic humans. Atherosclerosis. 2002;161:199–207. - PubMed
-
- Bunyan J, Mc HD, Green J, Marcinkiewicz S. Biological potencies of epsilon- and zeta-1-tocopherol and 5-methyltocol. Br J Nutr. 1961;15:253–257. - PubMed
-
- Dunphy PJ, Whittle KJ, Pennock JF, Morton RA. Identification and estimation of tocotrienols in Hevea latex. Nature. 1965;201:521–522.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

