Interleukin-1 as a phenotypic immunomodulator in keratinizing squamous metaplasia of the ocular surface in Sjögren's syndrome
- PMID: 20696775
- PMCID: PMC2928966
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2010.100227
Interleukin-1 as a phenotypic immunomodulator in keratinizing squamous metaplasia of the ocular surface in Sjögren's syndrome
Abstract
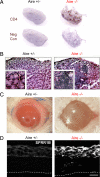
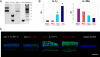
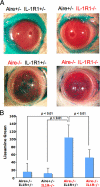
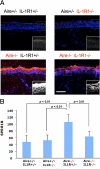
Chronic inflammation of the ocular surface in Sjögren's syndrome (SS) is associated with a vision-threatening, phenotypic change of the ocular surface, which converts from a nonkeratinized, stratified squamous epithelium to a nonsecretory, keratinized epithelium. This pathological process is known as squamous metaplasia. Based on a significant correlation between ocular surface interleukin (IL)-1beta expression and squamous metaplasia in patients with SS, we investigated the role of IL-1 in the pathogenesis of squamous metaplasia in an animal model that mimics the clinical characteristics of SS. Using autoimmune-regulator (aire)-deficient mice, we assessed lacrimal gland and ocular surface immunopathology by quantifying the infiltration of major histocompatibility complex class II(+) (I-A(d+)) dendritic cells and CD4(+) T cells. We examined squamous metaplasia using a biomarker of keratinization, small proline-rich protein 1B. We used lissamine green staining as a readout for ocular surface epitheliopathy and Alcian blue/periodic acid-Schiff histochemical analysis to characterize goblet cell muco-glycoconjugates. Within 8 weeks, the eyes of aire-deficient mice were pathologically keratinized with significant epithelial damage and altered mucin glycosylation. Although knockdown of IL-1 receptor 1 did not attenuate lymphocytic infiltration of the lacrimal gland or eye, it significantly reduced ocular surface keratinization, epitheliopathy, and muco-glycoconjugate acidification. These data demonstrate a phenotypic modulation role for IL-1 in the pathogenesis of squamous metaplasia and suggest that IL-1 receptor 1-targeted therapies may be beneficial for treating ocular surface disease associated with SS.
Figures




References
-
- Fox RI, Stern M, Michelson P. Update in Sjögren syndrome. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2000;12:391–398. - PubMed
-
- Mitsias DI, Kapsogeorgou EK, Moutsopoulos HM. The role of epithelial cells in the initiation and perpetuation of autoimmune lesions: lessons from Sjögren’s syndrome (autoimmune epithelitis). Lupus. 2006;15:255–261. - PubMed
-
- Tseng SC. Staging of conjunctival squamous metaplasia by impression cytology. Ophthalmology. 1985;92:728–733. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

