Dosage-sensitive regulation of cohesin chromosome binding and dynamics by Nipped-B, Pds5, and Wapl
- PMID: 20696838
- PMCID: PMC2950535
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00642-10
Dosage-sensitive regulation of cohesin chromosome binding and dynamics by Nipped-B, Pds5, and Wapl
Abstract
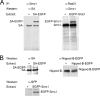
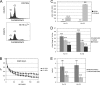
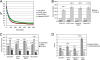
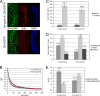
The cohesin protein complex holds sister chromatids together to ensure proper chromosome segregation upon cell division and also regulates gene transcription. Partial loss of the Nipped-B protein that loads cohesin onto chromosomes, or the Pds5 protein required for sister chromatid cohesion, alters gene expression and organism development, without affecting chromosome segregation. Knowing if a reduced Nipped-B or Pds5 dosage changes how much cohesin binds chromosomes, or the stability with which it binds, is critical information for understanding how cohesin regulates transcription. We addressed this question by in vivo fluorescence recovery after photobleaching (FRAP) with Drosophila salivary glands. Cohesin, Nipped-B, and Pds5 all bind chromosomes in both weak and stable modes, with residence half-lives of some 20 seconds and 6 min, respectively. Reducing the Nipped-B dosage decreases the amount of stable cohesin without affecting its chromosomal residence time, and reducing the Pds5 dosage increases the amount of stable cohesin. This argues that Nipped-B and Pds5 regulate transcription by controlling how much cohesin binds DNA in the stable mode, and not binding affinity. We also found that Nipped-B, Pds5, and the Wapl protein that interacts with Pds5 all play unique roles in cohesin chromosome binding.
Figures

References
-
- Arumugam, P., S. Gruber, K. Tanaka, C. H. Haering, K. Mechtler, and K. Nasmyth. 2003. ATP hydrolysis is required for cohesin's association with chromosomes. Curr. Biol. 13:1941-1953. - PubMed
-
- Bernard, P., J. Drogat, J. F. Maure, S. Dheur, S. Vaur, S. Genier, and J. P. Javerzat. 2006. A screen for cohesion mutants uncovers Ssl3, the fission yeast counterpart of the cohesin loading factor Scc4. Curr. Biol. 16:875-881. - PubMed
-
- Ciosk, R., M. Shirayama, A. Shevchenko, T. Tanaka, A. Toth, A. Shevchenko, and K. Nasmyth. 2000. Cohesin's binding to chromosomes depends on a separate complex consisting of Scc2 and Scc4 proteins. Mol. Cell 5:243-254. - PubMed
-
- Deardorff, M. A., M. Kaur, D. Yaeger, A. Rampuria, S. Korolev, J. Pie, C. Gil-Rodríguez, M. Arnedo, B. Loeys, A. D. Kline, M. Wilson, K. Lillquist, V. Siu, F. J. Ramos, A. Musio, L. S. Jackson, D. Dorsett, and I. D. Krantz. 2007. Mutations in cohesin complex members SMC3 and SMC1A cause a mild variant of Cornelia de Lange syndrome with predominant mental retardation. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 80:485-494. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
