Activities of high-dose daptomycin, vancomycin, and moxifloxacin alone or in combination with clarithromycin or rifampin in a novel in vitro model of Staphylococcus aureus biofilm
- PMID: 20696880
- PMCID: PMC2944618
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00455-10
Activities of high-dose daptomycin, vancomycin, and moxifloxacin alone or in combination with clarithromycin or rifampin in a novel in vitro model of Staphylococcus aureus biofilm
Abstract
Biofilm formation is an important virulence factor that allows bacteria to resist host responses and antibacterial agents. The aim of the study was to assess the in vitro activities of several antimicrobials alone or in combination against two Staphylococcus aureus isolates in a novel pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic (PK/PD) model of biofilm for 3 days. One methicillin-susceptible S. aureus strain (SH1000) and one methicillin-resistant S. aureus strain (N315) were evaluated in a modified biofilm reactor with polystyrene coupons. Simulated regimens included vancomycin (VAN) plus rifampin (RIF), moxifloxacin (MOX), and high doses (10 mg/kg of body weight/day) of daptomycin (DAP) alone or combined with RIF or clarithromycin (CLA). Against viable planktonic bacteria (PB) and biofilm-embedded bacteria (BB) of SH1000, neither DAP nor MOX alone was bactericidal. In contrast, the combination of DAP or MOX with CLA significantly increased the activity of the two agents against both PB and BB (P < 0.01), and DAP plus CLA reached the limit of detection at 72 h. Against PB of N315, DAP alone briefly achieved bactericidal activity at 24 h, whereas sustained bactericidal activity was observed at 32 h with VAN plus RIF. Overall, only a minimal reduction was observed with both regimens against BB (<2.8 log(10) CFU/ml). Finally, the combination of DAP and RIF was bactericidal against both PB and BB, achieving the limit of detection at 72 h. In conclusion, we developed a novel in vitro PK/PD model to assess the activities of antimicrobials against mature bacterial biofilm. Combinations of DAP or MOX with CLA were the most effective regimens and may represent promising options to treat persistent infections caused by S. aureus biofilms.
Figures
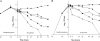

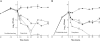
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of Ceftaroline Alone and in Combination against Biofilm-Producing Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus with Reduced Susceptibility to Daptomycin and Vancomycin in an In Vitro Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic Model.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015 Aug;59(8):4497-503. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00386-15. Epub 2015 May 18. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015. PMID: 25987623 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of High-Dose Daptomycin Versus Vancomycin Alone or Combined with Clarithromycin or Rifampin Against Staphylococcus aureus and S. epidermidis in a Novel In Vitro PK/PD Model of Bacterial Biofilm.Infect Dis Ther. 2014 Dec 18;4(1):51-65. doi: 10.1007/s40121-014-0055-5. Online ahead of print. Infect Dis Ther. 2014. PMID: 25519162 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Daptomycin Dose Exposure Alone or in Combination with β-Lactams or Rifampin against Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococci in an In Vitro Biofilm Model.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020 Apr 21;64(5):e02074-19. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02074-19. Print 2020 Apr 21. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020. PMID: 32094136 Free PMC article.
-
Pre-clinical Impact of the Synergistic Mechanism of Daptomycin and Ceftaroline on Patients with Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia Infections.Curr Rev Clin Exp Pharmacol. 2021;16(4):296-299. doi: 10.2174/1574884715666210108103813. Curr Rev Clin Exp Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33423652 Review.
-
Mechanisms of daptomycin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus: role of the cell membrane and cell wall.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2013 Jan;1277(1):139-58. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2012.06819.x. Epub 2012 Dec 5. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2013. PMID: 23215859 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Small lipopeptides possess anti-biofilm capability comparable to daptomycin and vancomycin.RSC Adv. 2015;5(73):59758-59769. doi: 10.1039/C5RA07896B. RSC Adv. 2015. PMID: 26257894 Free PMC article.
-
Rifamycin Derivatives Are Effective Against Staphylococcal Biofilms In Vitro and Elutable From PMMA.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015 Sep;473(9):2874-84. doi: 10.1007/s11999-015-4300-3. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015. PMID: 25896136 Free PMC article.
-
Polysaccharide intercellular adhesin in biofilm: structural and regulatory aspects.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2015 Feb 10;5:7. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2015.00007. eCollection 2015. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25713785 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treatment of late bacterial infections resulting from soft-tissue filler injections.Infect Drug Resist. 2019 Feb 20;12:469-480. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S186996. eCollection 2019. Infect Drug Resist. 2019. PMID: 30863129 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro Anti-Biofilm Activity of Bacteriophage K (ATCC 19685-B1) and Daptomycin against Staphylococci.Microorganisms. 2021 Aug 31;9(9):1853. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9091853. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 34576751 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aslam, S. 2008. Effect of antibacterials on biofilms. Am. J. Infect. Control 36:S175.e9-S175.e11. - PubMed
-
- Balfour, J. A., and L. R. Wiseman. 1999. Moxifloxacin. Drugs 57:363-373. - PubMed
-
- Cha, R., W. J. Brown, and M. J. Rybak. 2003. Bactericidal activities of daptomycin, quinupristin-dalfopristin, and linezolid against vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in an in vitro pharmacodynamic model with simulated endocardial vegetations. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 47:3960-3963. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

