TCF4 and CDX2, major transcription factors for intestinal function, converge on the same cis-regulatory regions
- PMID: 20696899
- PMCID: PMC2930576
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1003822107
TCF4 and CDX2, major transcription factors for intestinal function, converge on the same cis-regulatory regions
Abstract
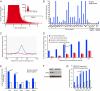
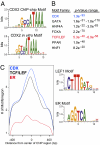
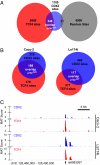
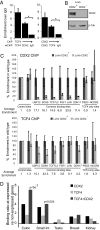
Surprisingly few pathways signal between cells, raising questions about mechanisms for tissue-specific responses. In particular, Wnt ligands signal in many mammalian tissues, including the intestinal epithelium, where constitutive signaling causes cancer. Genome-wide analysis of DNA cis-regulatory regions bound by the intestine-restricted transcription factor CDX2 in colonic cells uncovered highly significant overrepresentation of sequences that bind TCF4, a transcriptional effector of intestinal Wnt signaling. Chromatin immunoprecipitation confirmed TCF4 occupancy at most such sites and co-occupancy of CDX2 and TCF4 across short distances. A region spanning the single nucleotide polymorphism rs6983267, which lies within a MYC enhancer and confers colorectal cancer risk in humans, represented one of many co-occupied sites. Co-occupancy correlated with intestine-specific gene expression and CDX2 loss reduced TCF4 binding. These results implicate CDX2 in directing TCF4 binding in intestinal cells. Co-occupancy of regulatory regions by signal-effector and tissue-restricted transcription factors may represent a general mechanism for ubiquitous signaling pathways to achieve tissue-specific outcomes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- James R, Kazenwadel J. Homeobox gene expression in the intestinal epithelium of adult mice. J Biol Chem. 1991;266:3246–3251. - PubMed
-
- Mutoh H, et al. Conversion of gastric mucosa to intestinal metaplasia in Cdx2-expressing transgenic mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002;294:470–479. - PubMed
-
- Silberg DG, et al. Cdx2 ectopic expression induces gastric intestinal metaplasia in transgenic mice. Gastroenterology. 2002;122:689–696. - PubMed
-
- Liu T, et al. Regulation of Cdx2 expression by promoter methylation, and effects of Cdx2 transfection on morphology and gene expression of human esophageal epithelial cells. Carcinogenesis. 2007;28:488–496. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

