Cortical depth-specific microvascular dilation underlies laminar differences in blood oxygenation level-dependent functional MRI signal
- PMID: 20696904
- PMCID: PMC2930564
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1006735107
Cortical depth-specific microvascular dilation underlies laminar differences in blood oxygenation level-dependent functional MRI signal
Abstract
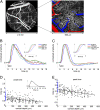
Changes in neuronal activity are accompanied by the release of vasoactive mediators that cause microscopic dilation and constriction of the cerebral microvasculature and are manifested in macroscopic blood oxygenation level-dependent (BOLD) functional MRI (fMRI) signals. We used two-photon microscopy to measure the diameters of single arterioles and capillaries at different depths within the rat primary somatosensory cortex. These measurements were compared with cortical depth-resolved fMRI signal changes. Our microscopic results demonstrate a spatial gradient of dilation onset and peak times consistent with "upstream" propagation of vasodilation toward the cortical surface along the diving arterioles and "downstream" propagation into local capillary beds. The observed BOLD response exhibited the fastest onset in deep layers, and the "initial dip" was most pronounced in layer I. The present results indicate that both the onset of the BOLD response and the initial dip depend on cortical depth and can be explained, at least in part, by the spatial gradient of delays in microvascular dilation, the fastest response being in the deep layers and the most delayed response in the capillary bed of layer I.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Brown GG, Perthen JE, Liu TT, Buxton RB. A primer on functional magnetic resonance imaging. Neuropsychol Rev. 2007;17:107–125. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- EB009118/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- EB00790/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS063226/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS057476/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB002066/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- P01 NS055104/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 EB009118/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- NS051188/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS036722/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS051188/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- EB2066/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS057476/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB000790/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS057198/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS-057198/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

