Association of retinal vascular endothelial growth factor with avascular retina in a rat model of retinopathy of prematurity
- PMID: 20697002
- PMCID: PMC3723353
- DOI: 10.1001/archophthalmol.2010.158
Association of retinal vascular endothelial growth factor with avascular retina in a rat model of retinopathy of prematurity
Abstract
Objective: To study the effects of oxygen fluctuations on rat vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), VEGF receptor 1(VEGFR1), and VEGFR2 in a model of retinopathy of prematurity (ROP).
Methods: Retinas at several postnatal days (p) were analyzed for VEGF splice variants, VEGFR1 and VEGFR2 messenger RNAs (mRNAs) using real-time polymerase chain reaction or for VEGF protein using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
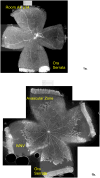
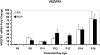
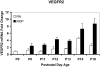
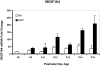
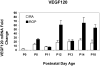
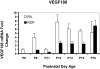
Results: Older developmental age was associated with VEGFR1 (P < .001), VEGF(120) (P < .001), and VEGF(188) (P = .03) mRNA overexpression. Expression of VEGFR2 and VEGF(164) mRNAs were associated with older age (P < .001) or exposure to the ROP model (P = .02 and P < .001, respectively). Expression of VEGF protein was greater at p14, when 30% avascular retina existed in the ROP model, compared with room air, when no avascular retina existed, and at p18, when intravitreous neovascularization existed in the model but not in room air (P < .001 for both).
Conclusions: Unlike models of oxygen-induced retinopathy that describe ROP before implementation of oxygen regulation, the ROP model re-creates oxygen stresses relevant to preterm infants with severe ROP today. Expression of VEGF(164) and VEGFR2 mRNAs and VEGF protein were increased in association with the ROP model and older developmental age and at time points when not only intravitreous neovascularization but also avascular retina were present in the ROP model and not in room air. Clinical Relevance Regulation of VEGF may have a role in the development of avascular retina and intravitreous neovascularization in some forms of severe ROP.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and pigment epithelial-derived factor in a rat model of retinopathy of prematurity.Mol Vis. 2011;17:1577-87. Epub 2011 Jun 10. Mol Vis. 2011. PMID: 21738387 Free PMC article.
-
Increased angiogenic factors associated with peripheral avascular retina and intravitreous neovascularization: a model of retinopathy of prematurity.Arch Ophthalmol. 2010 May;128(5):589-95. doi: 10.1001/archophthalmol.2010.65. Arch Ophthalmol. 2010. PMID: 20457980 Free PMC article.
-
Studies on the pathogenesis of avascular retina and neovascularization into the vitreous in peripheral severe retinopathy of prematurity (an american ophthalmological society thesis).Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 2010 Dec;108:96-119. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 2010. PMID: 21212851 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neutralizing antibody to VEGF reduces intravitreous neovascularization and may not interfere with ongoing intraretinal vascularization in a rat model of retinopathy of prematurity.Mol Vis. 2008 Feb 11;14:345-57. Mol Vis. 2008. PMID: 18334951 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of oxygen stresses on the development of features of severe retinopathy of prematurity: knowledge from the 50/10 OIR model.Doc Ophthalmol. 2010 Feb;120(1):25-39. doi: 10.1007/s10633-009-9181-x. Epub 2009 Jul 29. Doc Ophthalmol. 2010. PMID: 19639355 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Short hairpin RNA-mediated knockdown of VEGFA in Müller cells reduces intravitreal neovascularization in a rat model of retinopathy of prematurity.Am J Pathol. 2013 Sep;183(3):964-74. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2013.05.011. Am J Pathol. 2013. PMID: 23972394 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and pigment epithelial-derived factor in a rat model of retinopathy of prematurity.Mol Vis. 2011;17:1577-87. Epub 2011 Jun 10. Mol Vis. 2011. PMID: 21738387 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic polymorphisms of vascular endothelial growth factor and risk for retinopathy of prematurity in South of Iran.Mol Biol Rep. 2013 Jul;40(7):4613-8. doi: 10.1007/s11033-013-2554-y. Epub 2013 May 4. Mol Biol Rep. 2013. PMID: 23644986
-
Discovering Mechanisms in the Changing and Diverse Pathology of Retinopathy of Prematurity: The Weisenfeld Award Lecture.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2019 Apr 1;60(5):1286-1297. doi: 10.1167/iovs.18-25525. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2019. PMID: 30933256 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Breaking barriers: insight into the pathogenesis of neovascular age-related macular degeneration.Eye Brain. 2011;3:19-28. doi: 10.2147/EB.S24951. Epub 2011 Sep 27. Eye Brain. 2011. PMID: 27795668 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Terry TL. Extreme prematurity and fibroblastic overgrowth of persistent vascular sheath behind each crystalline lens:(1) Preliminary report. Am J Ophthalmol. 1942;25:203–204. - PubMed
-
- Patz A, Eastham A, Higginbotham DH, Kleh T. Oxygen studies in retrolental fibroplasia. Am J Ophthalmol. 1953;36:1511–1522. - PubMed
-
- Michaelson IC. The mode of development of the vascular system of the retina. With some observations on its significance for certain retinal diseases. Trans Ophthal Soc UK. 1948;68:137–180.
-
- Smith LEH, Wesolowski E, McLellan A, et al. Oxygen induced retinopathy in the mouse. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1994;35:101–111. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

