2009 H1N1 influenza: a twenty-first century pandemic with roots in the early twentieth century
- PMID: 20697263
- PMCID: PMC7119454
- DOI: 10.1097/MAJ.0b013e3181e937b0
2009 H1N1 influenza: a twenty-first century pandemic with roots in the early twentieth century
Abstract
A swine-origin H1N1 triple-reassortant influenza A virus found to be a distant relative of the 1918 "Spanish flu" virus emerged in April 2009 to give rise to the first influenza pandemic of the 21st century. Although disease was generally mild and similar to seasonal influenza, severe manifestations including respiratory failure were noted in some, particularly those with underlying conditions such as asthma, pregnancy and immunosuppression. Children and younger adults accounted for most cases, hospitalizations and deaths. A reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction assay was superior to antigen-based rapid tests for diagnosis. All 2009 H1N1 pandemic influenza strains were susceptible to 1 or more neuraminidase inhibitors. Monovalent, unadjuvanted 2009 H1N1 vaccines were licensed in the United States in September 2009 and initially targeted to younger individuals, pregnant women, caretakers of infants and healthcare providers. The 2009 H1N1 pandemic highlights the need for modernization of influenza vaccines, improved diagnostics and more rigorous evaluation of mitigation strategies.
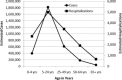
Figures

References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Isolation of avian influenza A (H5N1) viruses from humans—Hong Kong, May-December 1997. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 1997;46:1204–1207. - PubMed
-
- Novel Swine-Origin Influenza A (H1N1) Virus Investigation Team Emergence of a novel swine-origin influenza A (H1N1) virus in humans. N Engl J Med. 2009;25:2605–2615. - PubMed
-
- Zimmer S.M., Burke D.S. Historical perspective—emergence of influenza A (H11N1) viruses. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:279–285. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

