Bacteroides spp. and diarrhea
- PMID: 20697287
- PMCID: PMC3079340
- DOI: 10.1097/QCO.0b013e32833da1eb
Bacteroides spp. and diarrhea
Abstract
Purpose of review: The purpose of this review is to describe recent progress in the understanding of the role of Bacteroides spp. in human diarrheal diseases and newer murine studies implicating certain Bacteroides spp. in colorectal cancer.
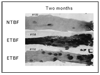
Recent findings: Bacteroides fragilis is the only strain of Bacteroides spp. associated with diarrheal disease. Toxin-producing strains of B. fragilis, termed enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis (ETBF), are an established cause of diarrheal disease in people. The clinical syndrome associated with ETBF diarrheal disease encompasses abdominal pain, tenesmus and inflammatory diarrhea. Two new studies conducted in mice have further defined the chronic inflammatory response associated with ETBF infection and observed that in the multiple intestinal neoplasia mouse strain, heterozygotes for the adenomatous polyposis coli gene, ETBF infection enhances development of colonic tumors. Separate murine studies have begun to define the role of nontoxin-producing B. fragilis as a symbiont, serving possibly to protect the host from colonic inflammation.
Summary: B. fragilis remains the leading anaerobe in human disease. ETBF is emerging as an important cause of human diarrheal disease but additional epidemiologic studies are needed to better understand the role of ETBF human disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Induction of persistent colitis by a human commensal, enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis, in wild-type C57BL/6 mice.Infect Immun. 2009 Apr;77(4):1708-18. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00814-08. Epub 2009 Feb 2. Infect Immun. 2009. PMID: 19188353 Free PMC article.
-
[Enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis as a factor in diarrhea].Mikrobiyol Bul. 2002 Jan;36(1):99-103. Mikrobiyol Bul. 2002. PMID: 12476774 Review. Turkish.
-
Enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis infection exacerbates tumorigenesis in AOM/DSS mouse model.Int J Med Sci. 2020 Jan 1;17(2):145-152. doi: 10.7150/ijms.38371. eCollection 2020. Int J Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 32038097 Free PMC article.
-
Enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis: A Possible Etiological Candidate for Bacterially-Induced Colorectal Precancerous and Cancerous Lesions.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020 Jan 17;9:449. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2019.00449. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32010637 Free PMC article.
-
Enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis: a rogue among symbiotes.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2009 Apr;22(2):349-69, Table of Contents. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00053-08. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2009. PMID: 19366918 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Defining Dysbiosis for a Cluster of Chronic Diseases.Sci Rep. 2019 Sep 9;9(1):12918. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-49452-y. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31501492 Free PMC article.
-
Microbiome Profiling Using Shotgun Metagenomic Sequencing Identified Unique Microorganisms in COVID-19 Patients With Altered Gut Microbiota.Front Microbiol. 2021 Oct 11;12:712081. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.712081. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34707577 Free PMC article.
-
crAssphage is not associated with diarrhoea and has high genetic diversity.Epidemiol Infect. 2016 Dec;144(16):3549-3553. doi: 10.1017/S095026881600176X. Epidemiol Infect. 2016. PMID: 30489235 Free PMC article.
-
Short-Term Lincomycin Exposure Depletion of Murine Microbiota Affects Short-Chain Fatty Acids and Intestinal Morphology and Immunity.Antibiotics (Basel). 2020 Dec 14;9(12):907. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics9120907. Antibiotics (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33327537 Free PMC article.
-
The Dysregulation of Polyamine Metabolism in Colorectal Cancer Is Associated with Overexpression of c-Myc and C/EBPβ rather than Enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis Infection.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016;2016:2353560. doi: 10.1155/2016/2353560. Epub 2016 Jun 28. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016. PMID: 27433286 Free PMC article.
References
-
-
Neish AS. Microbes in gastrointestinal health and disease. Gastroenterology. 2009;136:65–80. This is a comprehensive review of the role of the microbiome in promoting health and disease.
-
-
- Redondo MC, Arbo MD, Grindlinger J, Snydman DR. Attributable mortality of bacteremia associated with the Bacteroides fragilis group. Clin Infect Dis. 1995;20:1492–1496. - PubMed
-
- Polk BF, Kasper DL. Bacteroides fragilis subspecies in clinical isolates. Ann Intern Med. 1977;86:569–571. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

