Decreased IgA+ plasma cells and IgA expression in acute liver necrosis mice
- PMID: 20698046
- PMCID: PMC2921095
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i30.3827
Decreased IgA+ plasma cells and IgA expression in acute liver necrosis mice
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the number of intestinal immunoglobulin A (IgA+) plasma cells and expression of intestinal IgA in mice with acute liver necrosis.
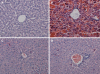
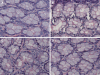
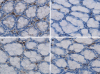
Methods: A model of acute liver necrosis was established by intraperitoneal injection of galactosamine (GalN) and lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Sixty mice were randomly divided into one of 4 equal groups: normal control, acute liver necrosis, LPS, or GalN. Hematoxylin and eosin staining, immunohistochemistry, and an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay were employed to assess liver and intestinal injury, count intestinal IgA+ plasma cells, and measure the expression level of IgA and interferon gamma (IFN-gamma) in the small intestinal mucosa of mice.
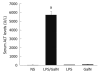
Results: Injured intestinal mucosa was observed in the acute liver necrosis group but not in the normal, LPS or GalN groups. Compared with the normal group, intestinal IgA+ plasma cells were slightly decreased in the LPS and GalN groups [429 +/- 20 per high power field (HPF), 406 +/- 18/HPF, respectively], whereas they were markedly decreased in the acute liver necrosis group (282 +/- 17/HPF vs 495 +/- 26/HPF in normal group, P < 0.05). The expression of intestinal IgA was also slightly decreased in LPS and GalN groups, but was markedly reduced in the acute liver necrosis group as determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (P < 0.05). In contrast, the level of IFN-gamma was slightly increased in LPS, GalN and acute liver necrosis groups, but with no statistical significance (P > 0.05).
Conclusion: Intestinal IgA+ plasma cells and IgA expression levels indicating that mucosal immune barrier dysfunction, does exist in acute liver necrosis.
Figures

References
-
- Deitch EA, Berg R. Bacterial translocation from the gut: a mechanism of infection. J Burn Care Rehabil. 1987;8:475–482. - PubMed
-
- Chiva M, Guarner C, Peralta C, Llovet T, Gómez G, Soriano G, Balanzó J. Intestinal mucosal oxidative damage and bacterial translocation in cirrhotic rats. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2003;15:145–150. - PubMed
-
- Kadaoui KA, Corthésy B. Secretory IgA mediates bacterial translocation to dendritic cells in mouse Peyer's patches with restriction to mucosal compartment. J Immunol. 2007;179:7751–7757. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

