Time course of congener uptake and elimination in rats after short-term inhalation exposure to an airborne polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB) mixture
- PMID: 20698547
- PMCID: PMC3408216
- DOI: 10.1021/es101274b
Time course of congener uptake and elimination in rats after short-term inhalation exposure to an airborne polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB) mixture
Abstract
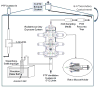
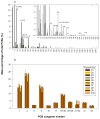
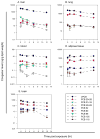
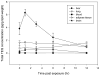
Despite the continued presence of PCBs in indoor and ambient air, few studies have investigated the inhalation route of exposure. While dietary exposure has declined, inhalation of the semivolatile, lower-chlorinated PCBs has risen in importance. We measured the uptake, distribution, and time course of elimination of inhaled PCB congeners to characterize the pulmonary route after short-term exposure. Vapor-phase PCBs were generated from Aroclor 1242 to a nose-only exposure system and characterized for congener levels and profiles. Rats were exposed via inhalation acutely (2.4 mg/m3 for 2 h) or subacutely (8.2 mg/m3, 2 hx10 days), after which pulmonary immune responses and PCB tissue levels were measured. Animals acutely exposed were euthanized at 0, 1, 3, 6, and 12 h post exposure to assess the time course of PCB uptake and elimination. Following rapid absorption and distribution, PCBs accumulated in adipose tissue but decayed in other tissues with half-lives increasing in liver (5.6 h)<lung (8.2 h)<brain (8.5 h)<blood (9.7 h). PCB levels were similar in lung, liver, and adipose tissue, lower in brain, and lowest in blood. Inhalation of the airborne PCB mixture contributed significantly to the body burden of lower-chlorinated congeners. Congeners detected in tissue were mostly ortho-substituted ranging from mono- to pentachlorobiphenyls. Selective uptake and elimination led to accumulation of a distinct congener spectrum in tissue. Minimal evidence of toxicity was observed.
Figures
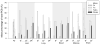
Similar articles
-
Subchronic inhalation exposure study of an airborne polychlorinated biphenyl mixture resembling the Chicago ambient air congener profile.Environ Sci Technol. 2012 Sep 4;46(17):9653-62. doi: 10.1021/es301129h. Epub 2012 Aug 24. Environ Sci Technol. 2012. PMID: 22846166 Free PMC article.
-
Congener-specific distribution of polychlorinated biphenyls in brain regions, blood, liver, and fat of adult rats following repeated exposure to Aroclor 1254.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1998 Dec;153(2):199-210. doi: 10.1006/taap.1998.8534. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1998. PMID: 9878591
-
Toxicity Evaluation of Exposure to an Atmospheric Mixture of Polychlorinated Biphenyls by Nose-Only and Whole-Body Inhalation Regimens.Environ Sci Technol. 2015 Oct 6;49(19):11875-83. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.5b02865. Epub 2015 Sep 22. Environ Sci Technol. 2015. PMID: 26348937 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of polychlorinated biphenyls on the nervous system.Toxicol Ind Health. 2000 Sep;16(7-8):305-33. doi: 10.1177/074823370001600708. Toxicol Ind Health. 2000. PMID: 11693948 Review.
-
A Review of Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs) Pollution in the Air: Where and How Much Are We Exposed to?Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Oct 26;19(21):13923. doi: 10.3390/ijerph192113923. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36360801 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comprehensive Subchronic Inhalation Toxicity Assessment of an Indoor School Air Mixture of PCBs.Environ Sci Technol. 2020 Dec 15;54(24):15976-15985. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.0c04470. Epub 2020 Nov 30. Environ Sci Technol. 2020. PMID: 33256405 Free PMC article.
-
Generation of Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance Using Hybrid Au-Ag Nanoparticle Arrays as a Sensor of Polychlorinated Biphenyls Detection.Sensors (Basel). 2016 Aug 5;16(8):1241. doi: 10.3390/s16081241. Sensors (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27527188 Free PMC article.
-
PAMAM dendrimers as nano carriers to investigate inflammatory responses induced by pulmonary exposure of PCB metabolites in Sprague-Dawley rats.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2016 Feb;23(3):2128-37. doi: 10.1007/s11356-015-5022-5. Epub 2015 Sep 24. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2016. PMID: 26400242 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome sequencing of 3,3',4,4',5-Pentachlorobiphenyl (PCB126)-treated human preadipocytes demonstrates progressive changes in pathways associated with inflammation and diabetes.Toxicol In Vitro. 2022 Sep;83:105396. doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2022.105396. Epub 2022 May 23. Toxicol In Vitro. 2022. PMID: 35618242 Free PMC article.
-
Headspace Extraction onto a 3D-Printed Device for GC-MS Quantification of Polychlorinated Biphenyls in Newborn Urine.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 19;26(6):2755. doi: 10.3390/ijms26062755. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40141397 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Harrad S, Hazrati S, Ibarra C. Concentrations of Polychlorinated Biphenyls in Indoor Air and Polybrominated Diphenyl Ehters in Indoor Air and Dust in Birmingham, United Kingdom: Implications for Human Exposure. Environ Sci Technol. 2006;40:4633–4638. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

