Describing the mechanism of antimicrobial peptide action with the interfacial activity model
- PMID: 20698568
- PMCID: PMC2955829
- DOI: 10.1021/cb1001558
Describing the mechanism of antimicrobial peptide action with the interfacial activity model
Abstract
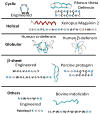
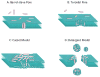
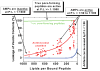
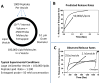
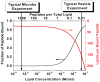
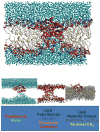
Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) have been studied for three decades, and yet a molecular understanding of their mechanism of action is still lacking. Here we summarize current knowledge for both synthetic vesicle experiments and microbe experiments, with a focus on comparisons between the two. Microbial experiments are done at peptide to lipid ratios that are at least 4 orders of magnitude higher than vesicle-based experiments. To close the gap between the two concentration regimes, we propose an "interfacial activity model", which is based on an experimentally testable molecular image of AMP-membrane interactions. The interfacial activity model may be useful in driving engineering and design of novel AMPs.
Figures
References
-
- Steiner H, Hultmark D, Engstrom A, Bennich H, Boman HG. Sequence and specificity of two antibacterial proteins involved in insect immunity. Nature (London) 1981;292:246–248. - PubMed
-
- Tossi A. Antimicrobial peptides datatbase. 2005. http://www.bbcm.units.it/~tossi/. Web Site.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

