Content of botulinum neurotoxin in Botox®/Vistabel®, Dysport®/Azzalure®, and Xeomin®/Bocouture®
- PMID: 20698714
- PMCID: PMC3586120
- DOI: 10.2165/11584780-000000000-00000
Content of botulinum neurotoxin in Botox®/Vistabel®, Dysport®/Azzalure®, and Xeomin®/Bocouture®
Abstract
Background: Botulinum neurotoxin type A (BoNT/A) is the active substance in preparations used for the highly effective treatment of neurologic disorders such as cervical dystonia, blepharospasm, or spasticity, as well as other indications such as axillary and palmar hyperhidrosis, and urologic disorders.
Objective: To determine the amount of BoNT/A protein present in pharmaceutical preparations of Botox®, Dysport®, and Xeomin®, which are identical with Vistabel®, Azzalure®, and Bocouture®, respectively.
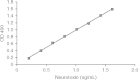
Methods: Rabbit and guinea pig antibodies raised against the 150 kD BoNT/A neurotoxin purified from Clostridium botulinum type A, strain ATCC 3502 ('Hall strain'), were used in a sensitive sandwich ELISA to determine the overall mean concentration of the 150 kD neurotoxin present in four batches of Botox® (C2344C3, C2384C3, C2419, and C2385), two batches of Dysport® (678F and 689X) and three batches of Xeomin® (61,111, 70,604, and 81,208). The specific neurotoxin potency, defined as the potency or biologic activity (units) per mass of neurotoxin protein (ng), was calculated based on the overall mean concentration of BoNT/A neurotoxin.
Results: Overall, the mean concentration of BoNT/A neurotoxin in Botox® was 0.73 ng per 100 unit vial (coefficient of variation [CV] = 3.5%), 3.24 ng per 500 unit vial of Dysport®, corresponding to 0.65 ng in 100 units (CV = 11.4%), and 0.44 ng per 100 unit vial of Xeomin® (CV = 1.9%). The specific potency of the 150 kD BoNT/A neurotoxin was calculated as 137 units/ng for Botox®, 154 units/ng Dysport®, and 227 units/ng Xeomin®.
Conclusions: The current study has shown that of the three products, Xeomin® contains the highest specific neurotoxin activity, followed by Dysport®, with Botox® having the lowest specific activity. This result suggests that Xeomin® contains only active neurotoxin in contrast with Botox®, which is likely to contain additional denatured/inactive neurotoxin.
Figures



Comment in
-
Is it possible to accurately determine content of botulinum neurotoxin type A in drug products?Drugs R D. 2010;10(2):91-2. doi: 10.2165/11584910-000000000-00000. Drugs R D. 2010. PMID: 20698717 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Consistent biochemical data are essential for comparability of botulinum toxin type A products.Drugs R D. 2011;11(1):97-8; author reply 98-9. doi: 10.2165/11590750-000000000-00000. Drugs R D. 2011. PMID: 21410299 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Jankovic J, Albanese A, Attassi MZ, et al. Botulinum toxintherapeutic clinical practice and science. Philadelphia (PA): Saunders Elsevier; 2009.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
