Transplantation of human adipose tissue-derived multilineage progenitor cells reduces serum cholesterol in hyperlipidemic Watanabe rabbits
- PMID: 20698754
- PMCID: PMC3030454
- DOI: 10.1089/ten.TEC.2010.0139
Transplantation of human adipose tissue-derived multilineage progenitor cells reduces serum cholesterol in hyperlipidemic Watanabe rabbits
Abstract
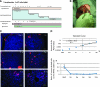
Familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) is an autosomal codominant disease characterized by high concentrations of proatherogenic lipoproteins and premature atherosclerosis secondary to low-density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor deficiency. We examined a novel cell therapy strategy for the treatment of FH in the Watanabe heritable hyperlipidemic (WHHL) rabbit, an animal model for homozygous FH. We delivered human adipose tissue-derived multilineage progenitor cells (hADMPCs) via portal vein and followed by immunosuppressive regimen to avoid xenogenic rejection. Transplantation of hADMPCs resulted in significant reductions in total cholesterol, and the reductions were observed within 4 weeks and maintained for 12 weeks. (125)I-LDL turnover study showed that the rate of LDL clearance was significantly higher in the WHHL rabbits with transplanted hADMPCs than those without transplanted. After transplantation hADMPCs were localized in the portal triad, subsequently integrated into the hepatic parenchyma. The integrated cells expressed human albumin, human alpha-1-antitrypsin, human Factor IX, human LDL receptors, and human bile salt export pump, indicating that the transplanted hADMPCs resided, survived, and showed hepatocytic differentiation in vivo and lowered serum cholesterol in the WHHL rabbits. These results suggested that hADMPC transplantation could correct the metabolic defects and be a novel therapy for inherited liver diseases.
Figures



References
-
- Brown M.S. Goldstein J.L. A receptor-mediated pathway for cholesterol homeostasis. Science. 1986;232:34. - PubMed
-
- Havel R.J. Yamada N. Shames D.M. Watanabe heritable hyperlipidemic rabbit. Animal model for familial hypercholesterolemia. Arteriosclerosis. 1989;9(1 Suppl):I33. - PubMed
-
- Bujo H. Takahashi K. Saito Y. Maruyama T. Yamashita S. Matsuzawa Y. Ishibashi S. Shionoiri F. Yamada N. Kita T. Clinical features of familial hypercholesterolemia in Japan in a database from 1996–1998 by the research committee of the ministry of health, labour and welfare of Japan. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2004;11:146. - PubMed
-
- Yamashita S. Hbujo H. Arai H. Harada-Shiba M. Matsui S. Fukushima M. Saito Y. Kita T. Matsuzawa Y. Long-term probucol treatment prevents secondary cardiovascular events: a cohort study of patients with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia in Japan. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2008;15:292. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
