Japanese encephalitis virus induces matrix metalloproteinase-9 in rat brain astrocytes via NF-κB signalling dependent on MAPKs and reactive oxygen species
- PMID: 20698853
- PMCID: PMC3010568
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.00982.x
Japanese encephalitis virus induces matrix metalloproteinase-9 in rat brain astrocytes via NF-κB signalling dependent on MAPKs and reactive oxygen species
Abstract
Background and purpose: Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV) is a member of the family Flaviviridae and JEV infection is a major cause of acute encephalopathy in children, which destroys cells in the CNS, including astrocytes and neurons. However, the detailed mechanisms underlying the inflammatory action of JEV are largely unclear.
Experimental approach: The effect of JEV on the expression of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-9 was determined by gelatin zymography, Western blot analysis, real-time PCR and promoter assay. The involvement of the NADPH oxidase and reactive oxygen species (ROS), MAPKs, and the transcription factor NF-κB in these responses was investigated by using selective pharmacological inhibitors and transfection with appropriate siRNAs.
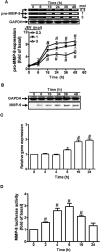
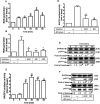
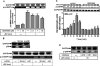
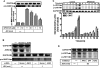
Key results: JEV induced the expression of the pro-form of MMP-9 in rat brain astrocytes (RBA-1 cells). In RBA-1 cells, JEV induced MMP-9 expression and promoter activity, which was inhibited by pretreatment with inhibitors of NADPH oxidase (diphenylene iodonium chloride or apocynin), MAPKs (U0126, SB203580 or SP600125) and a ROS scavenger (N-acetylcysteine), or transfection with siRNAs of p47(phox) , ERK1, JNK2 and p38. In addition, JEV-induced MMP-9 expression was reduced by pretreatment with an inhibitor of NF-κB (helenalin) or transfection with p65 siRNA. Moreover, JEV-stimulated NF-κB activation was inhibited by pretreatment with the inhibitors of NADPH oxidase and MAPKs.
Conclusions and implications: MMP-9 expression induced by JEV infection of RBA-1 cells was mediated through the generation of ROS and activation of p42/p44 MAPK, p38 MAPK and JNK1/2, leading to NF-κB activation.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Japanese encephalitis virus induces matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression via a ROS/c-Src/PDGFR/PI3K/Akt/MAPKs-dependent AP-1 pathway in rat brain astrocytes.J Neuroinflammation. 2012 Jan 18;9:12. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-9-12. J Neuroinflammation. 2012. PMID: 22251375 Free PMC article.
-
NADPH oxidase/ROS-dependent PYK2 activation is involved in TNF-α-induced matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression in rat heart-derived H9c2 cells.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2013 Oct 15;272(2):431-42. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2013.05.036. Epub 2013 Jun 14. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23774252
-
Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Rhamnetin on Bradykinin-Induced Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 Expression and Cell Migration in Rat Brain Astrocytes.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 6;23(2):609. doi: 10.3390/ijms23020609. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35054789 Free PMC article.
-
IL-1β Induces MMP-9-Dependent Brain Astrocytic Migration via Transactivation of PDGF Receptor/NADPH Oxidase 2-Derived Reactive Oxygen Species Signals.Mol Neurobiol. 2015 Aug;52(1):303-17. doi: 10.1007/s12035-014-8838-y. Epub 2014 Aug 27. Mol Neurobiol. 2015. PMID: 25159478
-
Pathogenicity and virulence of Japanese encephalitis virus: Neuroinflammation and neuronal cell damage.Virulence. 2021 Dec;12(1):968-980. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2021.1899674. Virulence. 2021. PMID: 33724154 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mouse Adenovirus Type 1 Early Region 1A Effects on the Blood-Brain Barrier.mSphere. 2016 Apr 20;1(2):e00079-16. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00079-16. eCollection 2016 Mar-Apr. mSphere. 2016. PMID: 27303733 Free PMC article.
-
Dengue Virus Infection of Blood-Brain Barrier Cells: Consequences of Severe Disease.Front Microbiol. 2019 Jun 26;10:1435. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.01435. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31293558 Free PMC article. Review.
-
West Nile virus-induced disruption of the blood-brain barrier in mice is characterized by the degradation of the junctional complex proteins and increase in multiple matrix metalloproteinases.J Gen Virol. 2012 Jun;93(Pt 6):1193-1203. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.040899-0. Epub 2012 Mar 7. J Gen Virol. 2012. PMID: 22398316 Free PMC article.
-
IL-1β promotes corneal epithelial cell migration by increasing MMP-9 expression through NF-κB- and AP-1-dependent pathways.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e57955. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0057955. Epub 2013 Mar 7. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23505448 Free PMC article.
-
MMPs and ADAMs in neurological infectious diseases and multiple sclerosis.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019 Aug;76(16):3097-3116. doi: 10.1007/s00018-019-03174-6. Epub 2019 Jun 6. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 31172218 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arai K, Lee SR, Lo EH. Essential role for ERK mitogen-activated protein kinase in matrix metalloproteinase-9 regulation in rat cortical astrocytes. Glia. 2003;43:254–264. - PubMed
-
- Barbieri SS, Cavalca V, Eligini S, Brambilla M, Caiani A, Tremoli E, et al. Apocynin prevents cyclooxygenase 2 expression in human monocytes through NADPH oxidase and glutathione redox-dependent mechanisms. Free Radic Biol Med. 2004;37:156–165. - PubMed
-
- Behren A, Simon C, Schwab RM, Loetzsch E, Brodbeck S, Huber E, et al. Papillomavirus E2 protein induces expression of the matrix metalloproteinase-9 via the extracellular signal-regulated kinase/activator protein-1 signaling pathway. Cancer Res. 2005;65:11613–11621. - PubMed
-
- Bian ZM, Elner SG, Yoshida A, Kunkel SL, Su J, Elner VM. Activation of p38, ERK1/2 and NIK pathways is required for IL-1beta and TNF-alpha-induced chemokine expression in human retinal pigment epithelial cells. Exp Eye Res. 2001;73:111–121. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

